Antibody (Suitable for clinical applications)
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:50-1:100 |
| Pretreatment | Citrate Buffer pH 6.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
Calcitonin Information for Pathologists
Summary:
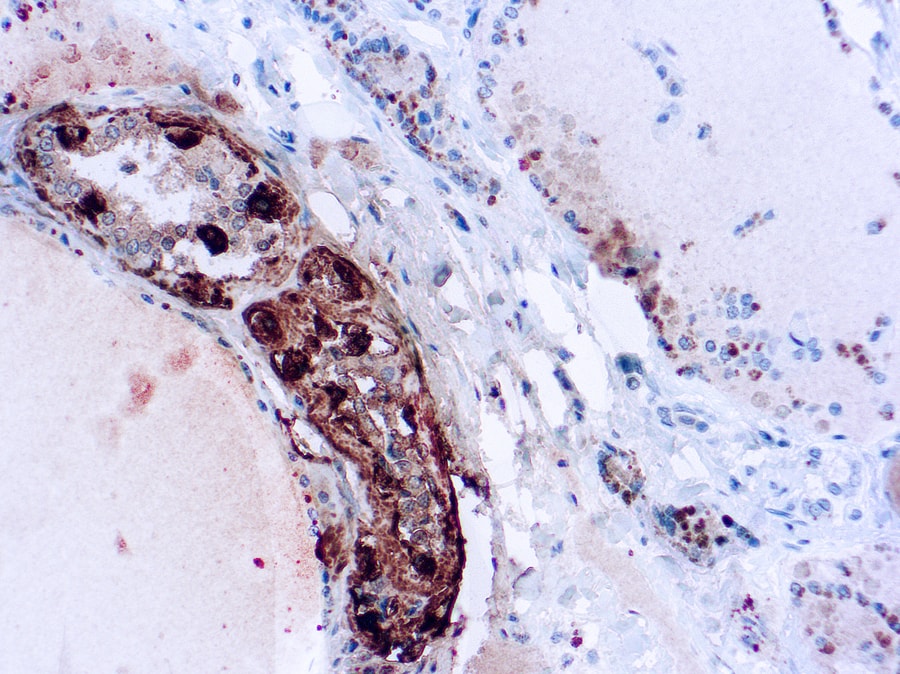
Calcitonin (thyrocalcitonin) is a 32 amino acid linear polypeptide hormone (molecular weight 3,421Kd) that participates in calcium and phosphorus metabolism. It is formed by the proteolytic cleavage of a larger pre-propeptide, which is a product of the CALC1 gene (CALC). In humans, it is primarily produced by the parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid. Other tissues such as the lungs and intestinal tract can also synthesize calcitonin. The calcitonin receptor protein has been shown to be a member of the seven transmembrane G protein coupled receptor family, which is coupled by G5 to adenylate cyclase and thereby to the generation of CAMP in target cells.
Common Uses By Pathologists:
As a marker for medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), especially when facing histologic subtypes such as the follicular, papillary or encapsulated variants that can pose diagnostic difficulties with follicular cellderived carcinomas and paraganglioma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008;132:359). Although highly specific, calcitonin staining may be patchy in medullary carcinomas and 5% of these tumors may be negative for this marker. In tumors with no staining and still suspected to be MTC, calcitonin and calcitonin generelated peptide mRNA can be demonstrated by in situ hybridization (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:207). To evaluate for C cell hyperplasia associated with familial MTC. High grade neuroendocrine tumors can also stain with calcitonin, and metastatic lesions can be misinterpreted as having arisen in the thyroid (Adv Anat Pathol 2004;11:202).
| Calcitonin General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 15.5 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| p15.2 [chr: 11] [chr_start: 14966668] [chr_end: 14972354] [strand: -1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | CALCA |
| Entrez Gene ID | 796 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001029124; NP_001732; XP_016873772; XP_016873773 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | ; NM_001033953; NM_001741; NM_001033952; XM_017018284; NR_125898; XM_017018283 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000011; NG_015960 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P01258 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA26029 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:796 |
| General Description of Calcitonin . | |
| This antibody recognizes calcitonin, which is a 32 amino acid peptide, which can be demonstrated in C cells of the normal and hyperplastic thyroid. Staining for calcitonin may be used for the identification of a spectrum of C cell proliferative abnormalities ranging from C cell hyperplasia to invasive tumors. Staining for calcitonin in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid produces a fine granular pattern in the cytoplasm. Amyloid deposits within the tumor may also exhibit varying degrees of calcitonin activity. | |




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.