Human Anti-CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A Antibody Product Attributes
CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in germinal center cells in the lymph node, tonsil. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in germinal center cells in the lymph node, tonsil. Low, but measureable presence of CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A could be seen inmelanocytes in skin. We were unable to detect CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A expression as measured by anti-CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| FCER2 Variability | + | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| CD23, FCER2, FCER2A, BLAST-2, CD23, FCE2, CD23A, CLEC4J, IGEBF | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | FCER2 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 2208 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000104921 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | XP_005272519, NP_001193948, NP_001207429, NP_001993 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | XM_005272462, NM_001207019, NM_001220500 NM_002002 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000019, NG_029554, NC_018930 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P06734, K3W4U1 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P06734, K3W4U1 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 3612 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | FCER2 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:2208 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA28058 |
| General Description of CD23 / FCER2 / FCER2A. | |
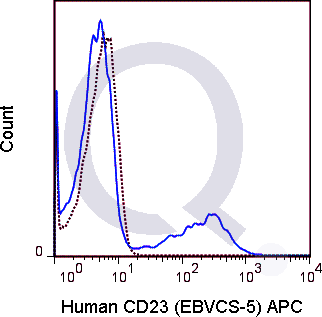
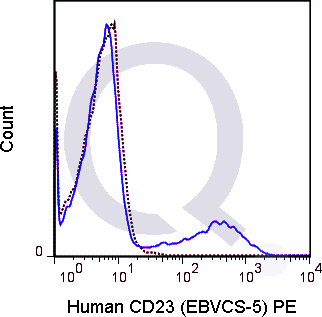
| The EBVCS-5 antibody is specific for human CD23, also known as the low affinity IgE receptor (FceRII), a 45 kDa type II transmembrane protein and member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is expressed on most B cells and is upregulated upon activation. It is also present on mantle zone B cells, eosinophils, monocytes and a subset of T cells and platelets. CD23 plays a role in B cell development and differentiation, and also functions to regulate IgE production. Soluble secreted forms of CD23 have been reported to bind IgE, stimulate release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from monocytes, and play a role in B cell differentiation. | |



There are no reviews yet.