Human Anti-CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin Antibody Product Attributes
CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-CD59 antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the golgi apparatus and vesicles.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
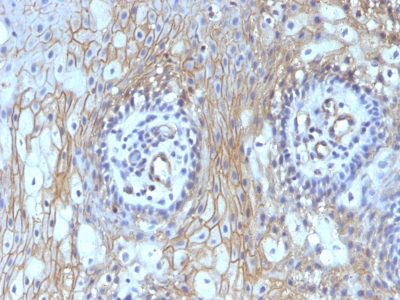
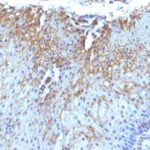
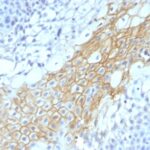
Variations in CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in endothelial cells in the colon and peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in endothelial cells in the colon and peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon. Low, but measureable presence of CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin could be seen inbile duct cells in the liver, cells in the granular layer in cerebellum, cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, cells in the tubules in kidney, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, fibroblasts in mesenchymal tissue, germinal center cells in the tonsil, glandular cells in the endometrium and stomach, glial cells in the caudate nucleus, keratinocytes in skin, macrophages in lung, melanocytes in skin, myocytes in skeletal muscle, neuropil in cerebral cortex, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix and uterine and oral mucosa. We were unable to detect CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin expression as measured by anti-CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | + | – | – | – | + | – | ++ | + | – | – | ++ | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | ++ | – |
| CD59 Variability | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ |
| CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| CD59, MAC-inhibitory protein, MAC-IP | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 20kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 11p13 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | CD59 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 966 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000085063 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001120699, NP_001120695, NP_976074, NP_976076, NP_001120698, NP_976075, NP_000602, NP_001120697 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_203330, NM_203331, NM_001127226, NM_001127223, NM_001127227, NM_001127225, NM_203329 NM_000611 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000011, NC_018922, NG_008057 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P13987, Q6FHM9 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P13987, Q6FHM9 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 1689 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | CD59 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:966 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA26228 |
| General Description of CD59 / Complement Regulatory Protein / Protectin. | |
| Reacts with human CD59, a 20kDa glycosyl phosphatidyl-inositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface protein. CD59 regulates complement-mediated cell lysis,, it is involved in lymphocyte signal transduction. This protein is a potent inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex, whereby it binds complement C8,/or C9 during the assembly of this complex, thereby inhibiting the incorporation of multiple copies of C9 into the complex, which is necessary for osmolytic pore formation. It inhibits formation of MAC, thus protecting cells from complement-mediated lysis. Genetic defects in GPI-anchor attachment, that cause a reduction or loss of CD59, CD55 on erythrocytes produce the symptoms of the disease paroxysmal hemoglobinuria (PNH). This MAb is useful for study on GPI-anchored proteins, PNH, CD59 functions. CD59 is widely distributed on cells in all tissues. The expression of CD59 on erythrocytes is important for their survival. | |



There are no reviews yet.