Human, Monkey, and Cat Anti-CD68 Antibody Product Attributes
CD68 Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-CD68 antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the vesicles and golgi apparatus.
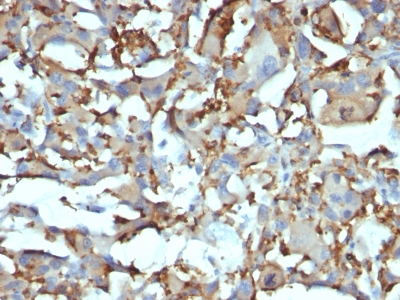
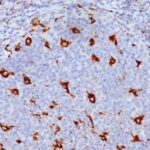
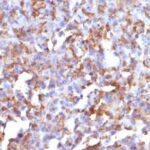
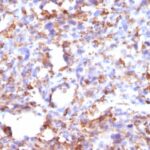
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in CD68 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in cells in the red pulp in spleen and macrophages in lung. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in cells in the red pulp in spleen and macrophages in lung. Low, but measureable presence of CD68 could be seen inglial cells in the cerebral cortex. We were unable to detect CD68 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
| CD68 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| CD68, Cluster of Differentiation 5, Macrosialin (mouse) | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 110kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 17p13.1 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | CD68 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 968 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000129226 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001242, NP_001035148 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001040059, NM_001251 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000017, NG_009204, NC_018928 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P34810 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P34810 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 1693 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | CD68 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:968 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA26232 |
| General Description of CD68. | |
| This antibody recognizes a glycoprotein of 110kDa, which is identified as CD68. It is important for identifying macrophages in tissue sections. It stains macrophages in a wide variety of human tissues, including Kupffer cells, macrophages in the red pulp of the spleen, in lamina propria of the gut, in lung alveoli,, in bone marrow. It reacts with myeloid precursors, peripheral blood granulocytes. It also reacts with plasmacytoid T cells, which are supposed to be of monocyte/macrophage origin. It shows strong granular cytoplasmic staining of chronic, acute myeloid leukemia, also reacts with rare cases of true histiocytic neoplasia. Lymphomas are negative or show few granules. | |




There are no reviews yet.