Human Anti-Cytokeratin 8 Anti-Human Antibody Product Attributes
Cytokeratin 8 Anti-Human Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
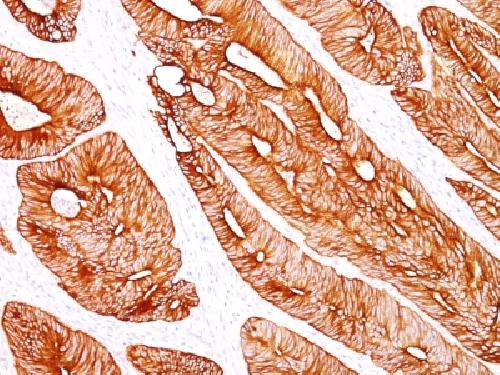
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Variations in Cytokeratin 8 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in bile duct cells in the liver, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, follicle cells in the ovary, glandular cells in the appendix, breast, cervix, uterine, duodenum, endometrium, epididymis, fallopian tube, gallbladder, prostate, rectum, seminal vesicle, small intestine, stomach and thyroid gland, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and nasopharynx, trophoblastic cells in the placenta and urothelial cells in the urinary bladder. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in bile duct cells in the liver, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, follicle cells in the ovary, glandular cells in the appendix, breast, cervix, uterine, duodenum, endometrium, epididymis, fallopian tube, gallbladder, prostate, rectum, seminal vesicle, small intestine, stomach and thyroid gland, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and nasopharynx, trophoblastic cells in the placenta and urothelial cells in the urinary bladder. Low, but measureable presence of Cytokeratin 8 could be seen in. We were unable to detect Cytokeratin 8 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of Cytokeratin 8 expression as measured by anti-Cytokeratin 8 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | – | – | +++ | ++ | – | – | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | – | +++ | + | +++ | +++ |
| KRT8 Variability | + | + | ++ | + | ++ | + | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | ++ |
| Cytokeratin 8 Anti-Human General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| CARD2, CK8, CYK8, CYKER, Cytokeratin Endo A, DreK8, EndoA, K2C8, K8, Keratin 8, KRT8, Type-II Keratin Kb8, anti-CARD2 antibody, anti-CK8 antibody, anti-CYK8 antibody, anti-CYKER antibody, anti-Cytokeratin Endo A antibody, anti-DreK8 antibody, anti-EndoA antibody, anti-K2C8 antibody, anti-K8 antibody, anti-Keratin 8 antibody, anti-KRT8 antibody, and anti-Type-II Keratin Kb8 antibody | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 52.5kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 12q13.13 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | KRT8 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 3856 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000170421 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001243211, NP_002264, NP_001243222 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NR_045962 NM_001256282, NM_001256293, NM_002273 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000012, NC_018923, NG_008402 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P05787, Q7L4M3 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P05787, Q7L4M3 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 6446 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | KRT8 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:3856 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA30234 |
| General Description of Cytokeratin 8 Anti-Human. | |
| Cytokeratin 8 (CK8) belongs to the type II (or B or basic) subfamily of high molecular weight cytokeratins and exists in combination with cytokeratin 18 (CK18). CK8 is primarily found in the non-squamous epithelia and is present in majority of adenocarcinomas and ductal carcinomas. It is absent in squamous cell carcinomas. Hepatocellular carcinomas are defined by the use of antibodies that recognize only cytokeratin 8 and 18. CK8 exists on several types of normal and neoplastic epithelia, including many ductal and glandular epithelia such as colon, stomach, small intestine, trachea, and esophagus as well as in transitional epithelium. Anti-CK8 does not react with skeletal muscle or nerve cells. Epithelioid sarcoma, chordoma, and adamantinoma show strong positivity corresponding to that of simple epithelia (with antibodies against CK8, CK18 and CK19). Reportedly, anti-CK8 is useful for the differentiation of lobular (ring-like, perinuclear ) from ductal (peripheral-predominant) carcinoma of the breast. | |


![Analysis of Mass Spec data (dashed-line) of fractions stained with Cytokeratin 8 Anti-Human MS-QAVA™ monoclonal antibody [Clone: K8/383] (solid-line), reveals that less than 13% of signal is attributable to non-specific binding of anti-Cytokeratin 8 Anti-Human [Clone: K8/383 ] to targets other than KRT8 protein. Even frequently cited antibodies have much greater non-specific interactions, averaging over 30%. Data in image is from analysis in Jurkat, U202 and HeLa cells.](https://cdn-enquirebio.pressidium.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/enQuire-Bio-3856-MSM3-P1-anti-Cytokeratin-8-Anti-Human-antibody.png)

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.