Antibody (Suitable for clinical applications)
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:50-1:100 |
| Pretreatment | Citrate Buffer pH 6.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
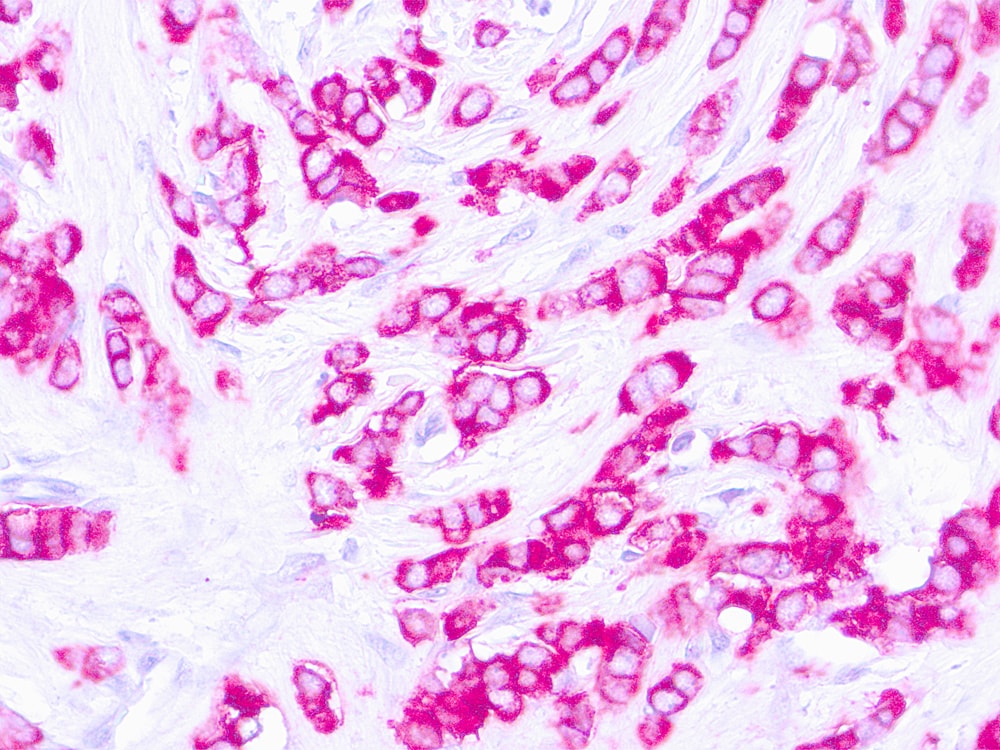
EpCAM Information for Pathologists
Summary:
Antibody to cell membrane glycoproteins expressed on healthy epithelia and in various carcinomas. Also known as epithelial cell adhesion molecule, BerEp4 (Ber-EP4, J Clin Pathol 1990;43:213), MOC31 (MOC-31, Acta Neuropathol 1991;83:46), CD326, TACSTD1 protein. MOC31 and BerEP4 are both anti-EpCAM antibodies, MOC31 appears to be superior (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2009;17:202). Anti-EpCam antibodies are in clinical trials for patients with cancer (Br J Cancer 2007;96:417). Uses by pathologists
Common Uses By Pathologists:
Membranous staining. Sensitive and specific for lung adenocarcinoma (positive) vs. mesothelioma (negative, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:43). May help distinguish, as part of a panel, hepatocellular carcinoma (usually negative) from metastatic adenocarcinoma to liver or cholangiocarcinoma (usually positive, Mod Pathol 2002;15:1279). Immunoexpression may predict poor survival in carcinomas of breast, gallbladder (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;129:424), ovary, pancreas. Microscopic (histologic) images
| EpCAM General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 34.9 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| p21 [chr: 2] [chr_start: 47345158] [chr_end: 47387601] [strand: 1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | EPCAM |
| Entrez Gene ID | 4072 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_002345 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_002354; |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_012352; NC_000002 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P16422 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA35493 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:4072 |
| Associated Diseases (KEGG IDs) | Diarrhea 5, with tufting enteropathy, congenital (DIAR5) [MIM:613217]: An intractable diarrhea of infancy characterized by villous atrophy and absence of inflammation, with intestinal epithelial cell dysplasia manifesting as focal epithelial tufts in the duodenum and jejunum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18572020}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer 8 (HNPCC8) [MIM:613244]: An autosomal dominant disease associated with marked increase in cancer susceptibility. It is characterized by a familial predisposition to early-onset colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and extra-colonic tumors of the gastrointestinal, urological and female reproductive tracts. HNPCC is reported to be the most common form of inherited colorectal cancer in the Western world. Clinically, HNPCC is often divided into two subgroups. Type I is characterized by hereditary predisposition to colorectal cancer, a young age of onset, and carcinoma observed in the proximal colon. Type II is characterized by increased risk for cancers in certain tissues such as the uterus, ovary, breast, stomach, small intestine, skin, and larynx in addition to the colon. Diagnosis of classical HNPCC is based on the Amsterdam criteria: 3 or more relatives affected by colorectal cancer, one a first degree relative of the other two; 2 or more generation affected; 1 or more colorectal cancers presenting before 50 years of age; exclusion of hereditary polyposis syndromes. The term ‘suspected HNPCC’ or ‘incomplete HNPCC’ can be used to describe families who do not or only partially fulfill the Amsterdam criteria, but in whom a genetic basis for colon cancer is strongly suspected. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19098912}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. HNPCC8 results from heterozygous deletion of 3-prime exons of EPCAM and intergenic regions directly upstream of MSH2, resulting in transcriptional read-through and epigenetic silencing of MSH2 in tissues expressing EPCAM. |
| General Description of EpCAM. | |
| This antibody reacts with an antigen of 265-400 kDa identified as epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) or MUC-1. EMA belonging to a heterogeneous group of heavily glycosylated proteins called human milk fat globule proteins. It stains both normal and neoplastic cells. Among normal epithelia, it reacts strongly with mammary epithelium and glandular epithelia but shows a patchy staining with squamous epithelium. | |



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.