Antibody (Suitable for clinical applications)
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:50-1:100 |
| Pretreatment | Citrate Buffer pH 6.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Information for Pathologists
Summary:
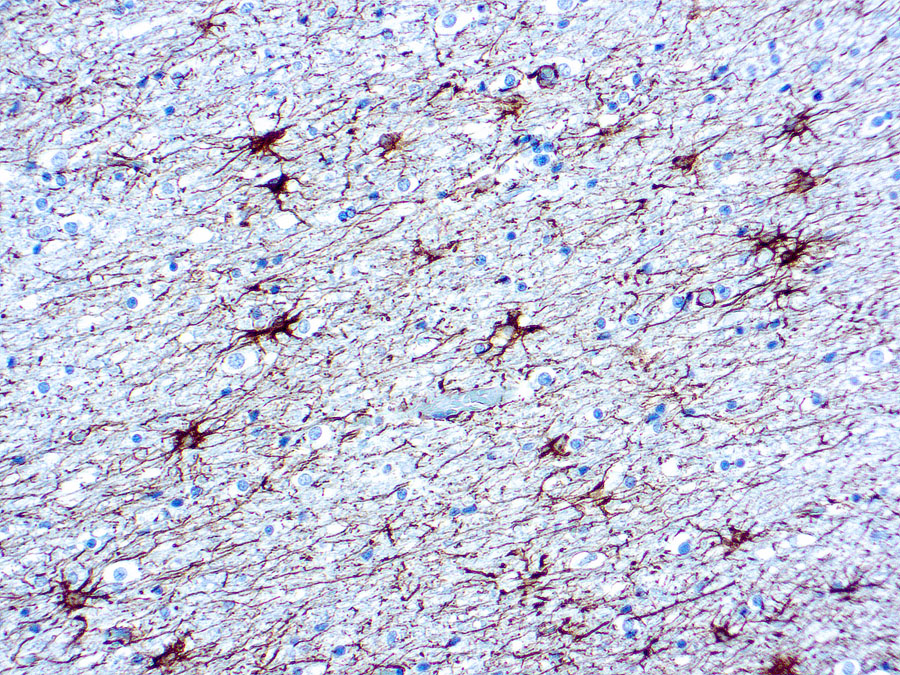
Intermediate filament for astrocytes (normal, reactive, neoplastic). Positive staining – disease CNS tumors, colonic schwannoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:846). Microscopic (histologic) images
Common Uses By Pathologists:
CNS tumors and colonic schwannoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:846) as well as myxopapillary ependymoma of broad ligament stain positive for GFAP.
| Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 49.9 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| q21.31 [chr: 17] [chr_start: 44903159] [chr_end: 44916937] [strand: -1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | GFAP |
| Entrez Gene ID | 2670 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001229305; NP_001124491; NP_002046 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | XM_024450691; NM_001363846; NM_002055; XM_024450693; XM_024450690; XM_024450692; NM_001242376; NM_001131019 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_008401; NC_000017 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P14136 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA28647 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:2670 |
| Associated Diseases (KEGG IDs) | Alexander disease (ALXDRD) [MIM:203450]: A rare disorder of the central nervous system. The most common form affects infants and young children, and is characterized by progressive failure of central myelination, usually leading to death within the first decade. Infants with Alexander disease develop a leukodystrophy with macrocephaly, seizures, and psychomotor retardation. Patients with juvenile or adult forms typically experience ataxia, bulbar signs and spasticity, and a more slowly progressive course. Histologically, Alexander disease is characterized by Rosenthal fibers, homogeneous eosinophilic inclusions in astrocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11138011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11567214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11595337, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12034785, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12034796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12581808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12944715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12975300, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15030911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15732097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17043438, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17805552, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17894839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17934883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17960815, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18004641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18079314, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19412928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20359319, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21917775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23364391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23743246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24742911}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| General Description of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein . | |
| This antibody reacts with the 52 kDa intermediate filament protein GFAP in brain and spinal cord. It labels some astrocytes and some CNS ependymal cells but not oligodendrocytes or neurons. This antibody does not react with other intermediate filament proteins. | |



There are no reviews yet.