Human and Macaque Monkey Anti-Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor Antibody Product Attributes
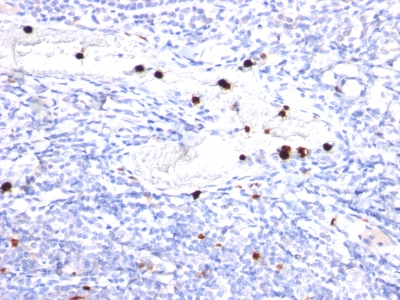
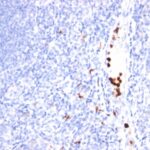
Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas. Low, but measureable presence of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor could be seen in cells in the endometrial stroma in endometrium, cells in the molecular layer in cerebellum, decidual cells in the placenta, germinal center cells in the tonsil, glandular cells in the adrenal gland, appendix, breast, gallbladder, parathyroid gland, prostate, rectum and thyroid gland, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, keratinocytes in skin, Langerhans in skin, Leydig cells in the testis, lymphoid tissue in appendix, macrophages in lung, neuronal cells in the caudate nucleus, cerebral cortex and hippocampus, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon, Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and nasopharynx, squamous epithelial cells in the tonsil, trophoblastic cells in the placenta and urothelial cells in the urinary bladder. We were unable to detect Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor expression as measured by anti-Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | ++ | ++ | – | + | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | + | + | ++ | – | + | – | – | + |
| CSF3 Variability | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1, IBP-1, placental protein 12, PP12, IGFBP1 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 19kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 17q21.1 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | CSF3 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 1440 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000108342 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_757373, NP_757374, NP_000750, NP_001171618 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_000759, NM_172220, NM_001178147, NM_172219, NR_033662 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_018928, NC_000017 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P09919, Q8N4W3, Q6FH65 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P09919, Q8N4W3, Q6FH65 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 2438 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | CSF3 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:1440 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA26941 |
| General Description of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor. | |
| This MAb recognizes granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) in the cytoplasm of mature granulocytes. It shows no reactivity with any other cell types. Markers of myeloid cells are useful in the identification of different levels of cellular differentiation. It reacts with early precursor, mature forms of myeloid cells. It is useful for the detection of myeloid leukemias, granulocytic sarcomas. It can be used as a marker of granulocytes in normal tissues or inflammatory processes.G-CSF is a pleiotropic cytokine that influences differentiation, proliferation, activation of the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. The human G-CSF cDNA encodes a 207 amino acid precursor containing a 29 amino acid signal peptide that is proteolytically cleaved to form a 178 amino acid residue mature protein. Two G-CSFs, which are identical except for a three amino acid deletion in the amino-terminus of one form of the protein have been isolated from human cells. Murine, human G-CSFs share 73% sequence identity at the amino acid level. | |



There are no reviews yet.