Human Anti-MAP3K1 Antibody Product Attributes
MAP3K1 Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-MAP3K1 antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the cytosol.
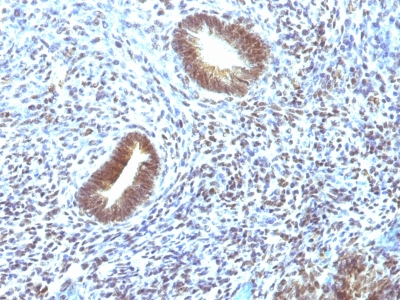
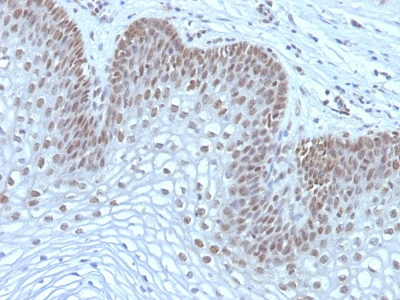
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in MAP3K1 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in decidual cells in the placenta, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, glandular cells in the adrenal gland, cervix, uterine, colon, duodenum, parathyroid gland and thyroid gland, hepatocytes in liver, macrophages in lung, myocytes in heart muscle, non-germinal center cells in the tonsil and respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and nasopharynx. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in decidual cells in the placenta, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, glandular cells in the adrenal gland, cervix, uterine, colon, duodenum, parathyroid gland and thyroid gland, hepatocytes in liver, macrophages in lung, myocytes in heart muscle, non-germinal center cells in the tonsil and respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and nasopharynx. Low, but measureable presence of MAP3K1 could be seen inadipocytes in mesenchymal tissue, bile duct cells in the liver, endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex, follicle cells in the ovary, glial cells in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, myocytes in skeletal muscle, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, peripheral nerve in mesenchymal tissue, pneumocytes in lung, smooth muscle cells in the smooth muscle and squamous epithelial cells in the oral mucosa. We were unable to detect MAP3K1 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of MAP3K1 expression as measured by anti-MAP3K1 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| MAP3K1 Variability | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| MAP3K1 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1, MAP3K1 | |
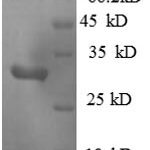
| Molecular Weight | |
| 195kDa (intact); 80kDa (cleaved) | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 5q11.2 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | MAP3K1 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 4214 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000095015 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_005912, XP_016864974, XP_016864973 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_005921, XM_017009485, XR_001742068, XM_017009484, |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000005, NC_018916, NG_031884 |
| UniProt ID(s) | Q13233 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Q13233 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 6848 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | MAP3K1 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:4214 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA30592 |
| General Description of MAP3K1. | |
| Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascades are activated by various extracellular stimuli, including growth factors. The MEK kinases (also designated MAP kinase kinase kinases, MKKKs, MAP3Ks or MEKKs) phosphorylate, thereby activate the MEKs (also called MAP kinase kinases or MKKs), including ERK, JNK, p38. These activated MEKs in turn phosphorylate, activate the MAP kinases. The MEK kinases include Raf-1, Raf-B, Mos, MEK kinase-1, MEK kinase-2, MEK kinase-3, MEK kinase-4, ASK 1 (MEK kinase- 5). MEK kinase-1 activates the ERK, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways by phosphorylation of MAP2K1, MAP2K4,, also activates the central protein kinases of the NF??B pathway, CHUK, IKBKB. Additionally, MEK kinase-1 uses an E3 ligase through its PHD domain, a RING-finger-like structure, to target proteins for degradation through ubiquitination. | |



There are no reviews yet.