Human Anti-MCM7 Antibody Product Attributes
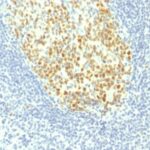
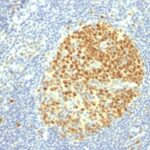
MCM7 Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Variations in MCM7 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, epidermal cells in the skin, germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil, glandular cells in the appendix, colon, duodenum, rectum and stomach, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus, oral mucosa, tonsil and vagina and trophoblastic cells in the placenta. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, epidermal cells in the skin, germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil, glandular cells in the appendix, colon, duodenum, rectum and stomach, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus, oral mucosa, tonsil and vagina and trophoblastic cells in the placenta. Low, but measureable presence of MCM7 could be seen infollicle cells in the ovary, glandular cells in the adrenal gland, endometrium, fallopian tube, parathyroid gland and salivary gland, Leydig cells in the testis, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and urothelial cells in the urinary bladder. We were unable to detect MCM7 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of MCM7 expression as measured by anti-MCM7 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| MCM7 Variability | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| MCM7 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| DNA replication licensing factor MCM7, MCM7 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 88kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 7q21.3-q22.1 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | MCM7 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 4176 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000166508 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | XP_016867706, NP_877577, XP_005250405, NP_001265524, NP_005907 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_182776, NM_001278595, XM_017012217, NM_005916, XM_005250348 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_018918, NC_000007 |
| UniProt ID(s) | C6EMX8, P33993, A0A0S2Z4A5 |
| UniGene ID(s) | C6EMX8, P33993, A0A0S2Z4A5 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 6950 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | MCM7 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:4176 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA30697 |
| General Description of MCM7. | |
| MCM7 is one of the highly conserved mini-chromosome maintenance proteins (MCM) that is essential for the initiation of eukaryotic genome replication. The hexameric protein complex formed by the MCM proteins is a key component of the pre-replication complex and may be involved in the formation of replication forks and in the recruitment of other DNA replication related proteins. The MCM complex consisting of this protein and MCM2, 4 and 6 proteins possesses DNA helicase activity, and may act as a DNA unwinding enzyme. Cyclin D1-dependent kinase, CDK4, is found to associate with this protein, and may regulate the binding of this protein with the tumor suppressor protein RB1/RB. | |

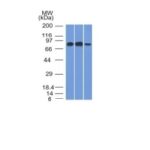
![MCM7 Antibody Mass Spec Validation Data Analysis of Mass Spec data (dashed-line) of fractions stained with MCM7 MS-QAVA™ monoclonal antibody [Clone: MCM7/1468] (solid-line), reveals that less than 3.8% of signal is attributable to non-specific binding of anti-MCM7 [Clone: MCM7/1468] to targets other than MCM7 protein. Even frequently cited antibodies have much greater non-specific interactions, averaging over 30%. Data in image is from analysis in A431, RT4 and MCF7 cells.](https://cdn-enquirebio.pressidium.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/enQuire-Bio-4176-MSM3-P0-anti-MCM7-antibody.png)



There are no reviews yet.