Human Anti-Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 Antibody Product Attributes
Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-S100A9 antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the cell junctions and cytosol.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
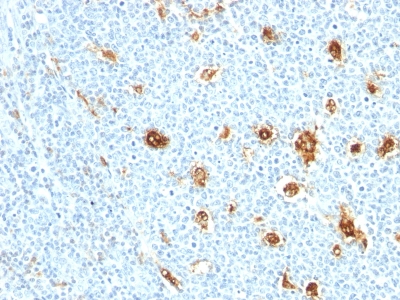
Variations in Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine, esophagus and oral mucosa, epidermal cells in the skin, cells in the red pulp in spleen and squamous epithelial cells in the tonsil and vagina. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine, esophagus and oral mucosa, epidermal cells in the skin, cells in the red pulp in spleen and squamous epithelial cells in the tonsil and vagina. Low, but measureable presence of Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 could be seen in cells in the white pulp in spleen. We were unable to detect Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 expression as measured by anti-Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | + | – | + | – | + | – | ++ | – | – | – | – | – | – | ++ | – | – | – | – |
| S100A9 Variability | ++ | + | ++ | + | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | + | ++ |
| Myeloid-Related Proteins 14 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| S100 calcium-binding protein A9, S100A9, migration inhibitory factor-related protein 14, MRP14, calgranulin B, S100A9 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 14kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 1q21 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | S100A9 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 6280 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000163220 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_002956 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_002965 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_018912, NC_000001 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P06702 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P06702 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 10499 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | S100A9 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:6280 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA34911 |
| General Description of Myeloid-Related Proteins 14. | |
| Recognizes a protein of14kDa, identified as MRP-14 (also known as Calgranulin B or S100AA9). It comprises 60% of the cytoplasmic protein fraction of circulating polymorphonuclear granulocytes, is also found in monocytes, macrophages, ileal tissue eosinophils. Peripheral blood monocytes carry the antigen extra-, intracellularly, neutrophils only intracellularly. It is a potent chemotactic factor for neutrophils. Plasma concentrations are elevated in diseases associated with increased neutrophil activity, like inflammatory bowel disease. Granulocytes terminate their existence after transmigration through the intestinal wall. Therefore, it is also detectable in feces. Elevated levels have been observed in body fluids such as plasma, saliva, gingival crevicular fluid, stools,, synovial fluid during infection, inflammatory conditions. This MAb reacts with neutrophils, monocytes,, macrophages,, has been shown as an important marker for identifying macrophages in tissue sections. | |



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.