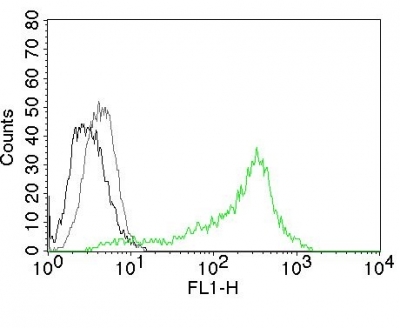
Human (-), Mouse (-), Rat (-), and Cow (-) Anti-Nucleolin Antibody Product Attributes
Nucleolin Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
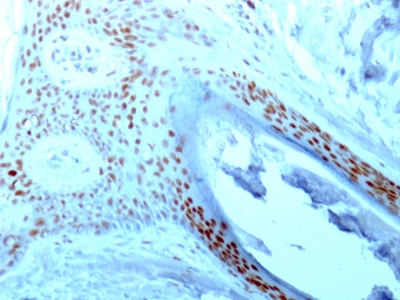
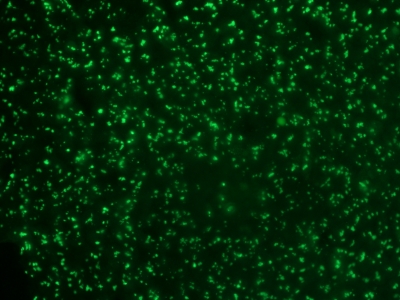
Anti-NCL antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the nucleoli and nucleus.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in Nucleolin antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in glandular cells in the adrenal gland and appendix, lymphoid tissue in appendix, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, adipocytes in breast, glandular cells in the breast, myoepithelial cells in the breast, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, glial cells in the caudate nucleus, neuronal cells in the caudate nucleus, cells in the granular layer in cerebellum, cells in the molecular layer in cerebellum, Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, glial cells in the cerebral cortex, neuronal cells in the cerebral cortex, glandular cells in the cervix, uterine, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine, endothelial cells in the colon, glandular cells in the colon, peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon, glandular cells in the duodenum, cells in the endometrial stroma in endometrium, glandular cells in the endometrium and epididymis, squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus, glandular cells in the fallopian tube and gallbladder, myocytes in heart muscle, glial cells in the hippocampus, neuronal cells in the hippocampus, cells in the glomeruli in kidney, cells in the tubules in kidney, bile duct cells in the liver, hepatocytes in liver, pneumocytes in lung, germinal center cells in the lymph node, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, respiratory epithelial cells in the nasopharynx, squamous epithelial cells in the oral mucosa, follicle cells in the ovary, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, islets of Langerhans in pancreas, glandular cells in the parathyroid gland, decidual cells in the placenta, trophoblastic cells in the placenta, glandular cells in the prostate, rectum, salivary gland and seminal vesicle, myocytes in skeletal muscle, fibroblasts in skin, keratinocytes in skin, Langerhans in skin, melanocytes in skin, epidermal cells in the skin, glandular cells in the small intestine, smooth muscle cells in the smooth muscle, adipocytes in mesenchymal tissue, chondrocytes in mesenchymal tissue, fibroblasts in mesenchymal tissue, peripheral nerve in mesenchymal tissue, non-germinal center cells in the tonsil, squamous epithelial cells in the tonsil, urothelial cells in the urinary bladder, squamous epithelial cells in the vagina, cells in the red pulp in spleen, cells in the white pulp in spleen, glandular cells in the stomach, cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, Leydig cells in the testis, glandular cells in the thyroid gland and germinal center cells in the tonsil. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in glandular cells in the adrenal gland and appendix, lymphoid tissue in appendix, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, adipocytes in breast, glandular cells in the breast, myoepithelial cells in the breast, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, glial cells in the caudate nucleus, neuronal cells in the caudate nucleus, cells in the granular layer in cerebellum, cells in the molecular layer in cerebellum, Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, glial cells in the cerebral cortex, neuronal cells in the cerebral cortex, glandular cells in the cervix, uterine, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine, endothelial cells in the colon, glandular cells in the colon, peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon, glandular cells in the duodenum, cells in the endometrial stroma in endometrium, glandular cells in the endometrium and epididymis, squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus, glandular cells in the fallopian tube and gallbladder, myocytes in heart muscle, glial cells in the hippocampus, neuronal cells in the hippocampus, cells in the glomeruli in kidney, cells in the tubules in kidney, bile duct cells in the liver, hepatocytes in liver, pneumocytes in lung, germinal center cells in the lymph node, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, respiratory epithelial cells in the nasopharynx, squamous epithelial cells in the oral mucosa, follicle cells in the ovary, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, islets of Langerhans in pancreas, glandular cells in the parathyroid gland, decidual cells in the placenta, trophoblastic cells in the placenta, glandular cells in the prostate, rectum, salivary gland and seminal vesicle, myocytes in skeletal muscle, fibroblasts in skin, keratinocytes in skin, Langerhans in skin, melanocytes in skin, epidermal cells in the skin, glandular cells in the small intestine, smooth muscle cells in the smooth muscle, adipocytes in mesenchymal tissue, chondrocytes in mesenchymal tissue, fibroblasts in mesenchymal tissue, peripheral nerve in mesenchymal tissue, non-germinal center cells in the tonsil, squamous epithelial cells in the tonsil, urothelial cells in the urinary bladder, squamous epithelial cells in the vagina, cells in the red pulp in spleen, cells in the white pulp in spleen, glandular cells in the stomach, cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, Leydig cells in the testis, glandular cells in the thyroid gland and germinal center cells in the tonsil. Low, but measureable presence of Nucleolin could be seen in. We were unable to detect Nucleolin in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
| Nucleolin General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| NCL, Nucleolin, anti-Nucleolin antibody | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 76kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 2q37.1 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | NCL |
| Entrez Gene ID | 4691 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000115053 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_005372 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_005381 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000002, NC_018913 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P19338, A0A024R4A0, B3KM80 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P19338, A0A024R4A0, B3KM80 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 7667 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | NCL |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:4691 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA31469 |
| General Description of Nucleolin. | |
| Recognizes a protein of ~76kDa, which is identified as Nucleolin (NCL). It is the major nucleolar phosphoprotein of growing eukaryotic cells. NCL is located mainly in dense fibrillar regions of the nucleolus. It is found associated with intranucleolar chromatin, pre-ribosomal particles. Human NCL gene consists of 14 exons with 13 introns, spans approximately 11kb. It induces chromatin decondensation by binding to histone H1. It is thought to play a role in pre-rRNA transcription, ribosome assembly.This MAb can be used to stain the nucleoli in cell or tissue preparations, can be used as a marker of the nucleoli in subcellular fractions. It produces a speckled pattern in the nuclei of cells of normal, malignant cells, may be used to stain the nucleoli of cells in fixed or frozen tissue sections. It can be used with paraformaldehyde fixed frozen tissue or cell preparations, formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections. | |



There are no reviews yet.