Antibody (Suitable for clinical applications)
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:50-1:100 |
| Pretreatment | EDTA Buffer pH 8.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
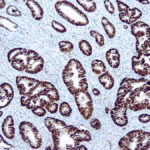
p53 Information for Pathologists
Summary:
Tumor suppressor gene at 17p13, 53 kDa. p53 ensures that cells repair any damaged DNA before cell division by inducing cell cycle arrest to allow time for:. DNA repair OR. To force the cell to undergo apoptosis via activation of bax gene (J Biomed Biotechnol 2011;2011:603925, Wikipedia – p53). Mutations are among most commonly detected genetic abnormalities in human neoplasia; however, presence of p53 mutation is usually not, by itself, specific enough for a diagnosis for malignancy, and its absence does not rule out malignancy.
Common Uses By Pathologists:
Differentiate malignant conditions, which are often p53+ (carcinoma in situ of urothelium and other sites, invasive carcinoma) from reactive and metaplastic conditions which are usually p53- (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1074). May be useful to distinguish uterine serous carcinoma (p53+) from endometrioid carcinoma (usually p53-). May be useful as serum tumor marker (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:1570). Microscopic (histologic) images Images hosted on PathOut server:.
| p53 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 43.7 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| p13.1 [chr: 17] [chr_start: 7661779] [chr_end: 7687550] [strand: -1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | TP53 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 7157 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001119585; NP_001119586; NP_001119587; NP_001119588; NP_001263624; NP_001263627; NP_001119589; NP_001263625; NP_001263628; NP_001263689; NP_001263690; NP_001263626; NP_001119590; NP_000537; NP_001119584 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001126112; NM_001276697; NM_001126115; NM_001126114; NM_001276698; NM_001276761; NM_001126118; NM_001126113; NM_001126117; NM_001276695; NM_001276699; NM_001276760; NM_000546; NM_001126116; NM_001276696 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000017; NG_017013 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P04637 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA36679 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:7157 |
| Associated Diseases (KEGG IDs) | TP53 is found in increased amounts in a wide variety of transformed cells. TP53 is frequently mutated or inactivated in about 60% of cancers. TP53 defects are found in Barrett metaplasia a condition in which the normally stratified squamous epithelium of the lower esophagus is replaced by a metaplastic columnar epithelium. The condition develops as a complication in approximately 10% of patients with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease and predisposes to the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma.; Esophageal cancer (ESCR) [MIM:133239]: A malignancy of the esophagus. The most common types are esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Cancer of the esophagus remains a devastating disease because it is usually not detected until it has progressed to an advanced incurable stage. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) [MIM:151623]: An autosomal dominant familial cancer syndrome that in its classic form is defined by the existence of a proband affected by a sarcoma before 45 years with a first degree relative affected by any tumor before 45 years and another first degree relative with any tumor before 45 years or a sarcoma at any age. Other clinical definitions for LFS have been proposed and called Li-Fraumeni like syndrome (LFL). In these families affected relatives develop a diverse set of malignancies at unusually early ages. Four types of cancers account for 80% of tumors occurring in TP53 germline mutation carriers: breast cancers, soft tissue and bone sarcomas, brain tumors (astrocytomas) and adrenocortical carcinomas. Less frequent tumors include choroid plexus carcinoma or papilloma before the age of 15, rhabdomyosarcoma before the age of 5, leukemia, Wilms tumor, malignant phyllodes tumor, colorectal and gastric cancers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10484981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1565144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1737852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1933902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1978757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2259385, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7887414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8825920, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452042}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) [MIM:275355]: A non-melanoma skin cancer affecting the head and neck. The hallmark of cutaneous SCC is malignant transformation of normal epidermal keratinocytes. The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.; Lung cancer (LNCR) [MIM:211980]: A common malignancy affecting tissues of the lung. The most common form of lung cancer is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that can be divided into 3 major histologic subtypes: squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and large cell lung cancer. NSCLC is often diagnosed at an advanced stage and has a poor prognosis. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Papilloma of choroid plexus (CPP) [MIM:260500]: A benign tumor of neuroectodermal origin that generally occurs in childhood, but has also been reported in adults. Although generally found within the ventricular system, choroid plexus papillomas can arise ectopically in the brain parenchyma or disseminate throughout the neuraxis. Patients present with signs and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure including headache, hydrocephalus, papilledema, nausea, vomiting, cranial nerve deficits, gait impairment, and seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12085209}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Adrenocortical carcinoma (ADCC) [MIM:202300]: A malignant neoplasm of the adrenal cortex and a rare childhood tumor. It occurs with increased frequency in patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Li-Fraumeni syndrome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11481490}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Basal cell carcinoma 7 (BCC7) [MIM:614740]: A common malignant skin neoplasm that typically appears on hair-bearing skin, most commonly on sun-exposed areas. It is slow growing and rarely metastasizes, but has potentialities for local invasion and destruction. It usually develops as a flat, firm, pale area that is small, raised, pink or red, translucent, shiny, and waxy, and the area may bleed following minor injury. Tumor size can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21946351}. Disease susceptibility is associated with variations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Bone marrow failure syndrome 5 (BMFS5) [MIM:618165]: A form of bone marrow failure syndrome, a heterogeneous group of life-threatening disorders characterized by hematopoietic defects in association with a range of variable extra hematopoietic features. BMFS5 is an autosomal dominant form characterized by infantile onset of severe red cell anemia requiring transfusion. Additional features include hypogammaglobulinemia, poor growth with microcephaly, developmental delay, and seizures. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30146126}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| General Description of p53 . | |
| p53 acts as both a tumor-suppressor and transcription factor that, upon activation by DNA damage and other cellular stress signals, leads to the transcription of genes triggering cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and DNA repair. p53 is overexpressed in over 50% of human cancers. Positive staining of p53 detected by immunohistochemistry has been observed in colon cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer and ovary cancer. | |




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.