Human Anti-Parathyroid Hormone Antibody Product Attributes
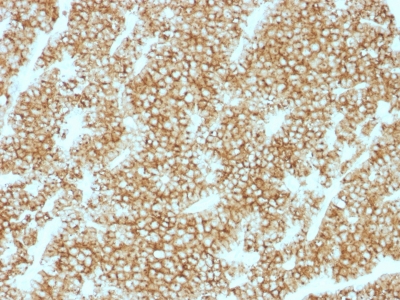
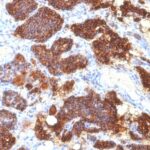
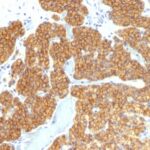
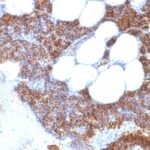
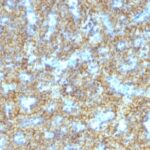
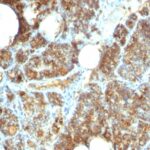
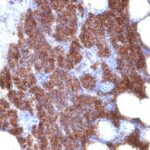
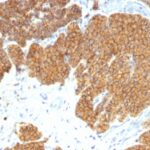
Parathyroid Hormone Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in Parathyroid Hormone antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in glandular cells in the parathyroid gland. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in glandular cells in the parathyroid gland. Low, but measureable presence of Parathyroid Hormone could be seen in. We were unable to detect Parathyroid Hormone in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
| Parathyroid Hormone General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Parathyroid Hormone, PTH | |
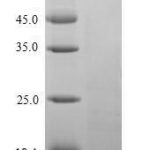
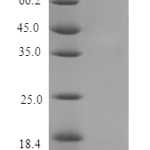
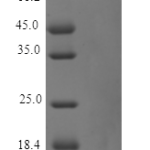
| Molecular Weight | |
| 9kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 11p15.3-p15.1 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | PTH |
| Entrez Gene ID | 5741 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000152266 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_000306, NP_001303281 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_000315, NM_001316352 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_008962, NC_018922, NC_000011 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P01270 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P01270 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 9606 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | PTH |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:5741 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA33951 |
| General Description of Parathyroid Hormone. | |
| Epitope of this MAb maps in the N-terminus of PTH, a hormone produced by the parathyroid gland that regulates the concentration of calcium and phosphorus in extracellular fluid. This hormone elevates blood Ca2+ levels by dissolving the salts in bone and preventing their renal excretion. It is produced in the parathyroid gland as an 84 amino acid single chain polypeptide. It can also be secreted as N-terminal truncated fragments or C-terminal fragments after intracellular degradation, as in case of hypercalcemia. Defects in this gene are a cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism (FIH); also called autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism or autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. FIH is characterized by hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia due to inadequate secretion of parathyroid hormone. Symptoms are seizures, tetany and cramps. FIH exist both as autosomal dominant and recessive forms of hypoparathyroidism. | |




There are no reviews yet.