Human and Rat Anti-SUMO-2 Antibody Product Attributes
SUMO-2 Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
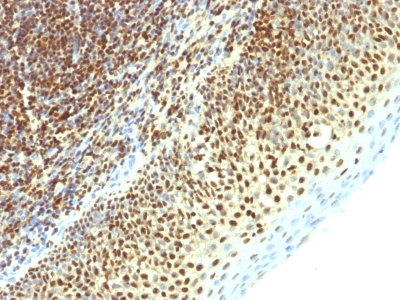
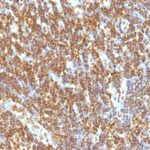
Anti-SUMO2 antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the nuclear bodies and nucleoplasm.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in SUMO-2 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in glandular cells in the adrenal gland, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, glandular cells in the breast, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, glandular cells in the cervix, uterine, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine, cells in the endometrial stroma in endometrium, glandular cells in the endometrium and epididymis, squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus, glandular cells in the fallopian tube and gallbladder, pneumocytes in lung, respiratory epithelial cells in the nasopharynx, squamous epithelial cells in the oral mucosa, follicle cells in the ovary, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, decidual cells in the placenta, trophoblastic cells in the placenta, glandular cells in the prostate, salivary gland and seminal vesicle, fibroblasts in skin, keratinocytes in skin, Langerhans in skin, melanocytes in skin, epidermal cells in the skin, fibroblasts in mesenchymal tissue, cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, urothelial cells in the urinary bladder and squamous epithelial cells in the vagina. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in glandular cells in the adrenal gland, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, glandular cells in the breast, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, glandular cells in the cervix, uterine, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine, cells in the endometrial stroma in endometrium, glandular cells in the endometrium and epididymis, squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus, glandular cells in the fallopian tube and gallbladder, pneumocytes in lung, respiratory epithelial cells in the nasopharynx, squamous epithelial cells in the oral mucosa, follicle cells in the ovary, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, decidual cells in the placenta, trophoblastic cells in the placenta, glandular cells in the prostate, salivary gland and seminal vesicle, fibroblasts in skin, keratinocytes in skin, Langerhans in skin, melanocytes in skin, epidermal cells in the skin, fibroblasts in mesenchymal tissue, cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, urothelial cells in the urinary bladder and squamous epithelial cells in the vagina. Low, but measureable presence of SUMO-2 could be seen inglandular cells in the appendix, adipocytes in breast, glial cells in the caudate nucleus, neuronal cells in the caudate nucleus, cells in the granular layer in cerebellum, cells in the molecular layer in cerebellum, Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex, glial cells in the cerebral cortex, peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon, glial cells in the hippocampus, neuronal cells in the hippocampus, bile duct cells in the liver, hepatocytes in liver, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, islets of Langerhans in pancreas, glandular cells in the parathyroid gland, peripheral nerve in mesenchymal tissue, cells in the red pulp in spleen, cells in the white pulp in spleen and germinal center cells in the tonsil. We were unable to detect SUMO-2 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
| SUMO-2 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2, SUMO2, SUMO-2 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 11-13kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 17q25.1 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | SUMO2 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 6613 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000188612 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001005849, NP_008868 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001005849, NM_006937 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000017, NC_018928 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P55855, A0A024R8S3, P61956 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P55855, A0A024R8S3, P61956 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 11125 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | SUMO2 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:6613 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA134914683 |
| General Description of SUMO-2. | |
| The small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) proteins, which include SUMO-1, 2, 3, belong to the ubiquitin-like protein family. Like ubiquitin, the SUMO proteins are synthesized as precursor proteins that undergo processing before conjugation to target proteins. Also, both utilize the E1, E2, E3 cascade enzymes for conjugation. However, SUMO, ubiquitin differ with respect to targeting. Ubiquitination predominantly targets proteins for degradation, whereas sumoylation targets proteins to a variety of cellular processing, including nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability. The unconjugated SUMO-1, 2, 3 proteins localize to the nuclear membrane, nuclear bodies, cytoplasm, respectively. SUMO-1 utilizes Ubc9 for conjugation to several target proteins, which include MDM2, p53, PML, RanGap1. SUMO-2, 3 contribute to a greater percentage of protein modification than does SUMO-1, unlike SUMO-1, they can form polymeric chains. In addition, SUMO-3 regulates beta-Amyloid generation, may be critical in the onset or progression of Alzheimer s disease. | |



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.