Human Anti-TIMP2 Antibody Product Attributes
TIMP2 Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
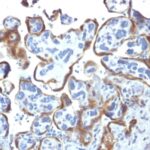
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in TIMP2 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. Low, but measureable presence of TIMP2 could be seen inglandular cells in the appendix, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, glial cells in the caudate nucleus, neuronal cells in the cerebral cortex, glandular cells in the colon, peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon, glandular cells in the endometrium, squamous epithelial cells in the esophagus, glandular cells in the gallbladder, myocytes in heart muscle, neuronal cells in the hippocampus, hepatocytes in liver, pneumocytes in lung, germinal center cells in the lymph node, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, respiratory epithelial cells in the nasopharynx, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, decidual cells in the placenta, glandular cells in the rectum, myocytes in skeletal muscle, Langerhans in skin, melanocytes in skin, smooth muscle cells in the smooth muscle, adipocytes in mesenchymal tissue, cells in the red pulp in spleen, glandular cells in the stomach, non-germinal center cells in the tonsil and squamous epithelial cells in the vagina. We were unable to detect TIMP2 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of TIMP2 expression as measured by anti-TIMP2 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | ++ | + | + | + | + | – | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| TIMP2 Variability | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ |
| TIMP2 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2, TIMP2 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 21kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 17q25 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | TIMP2 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 7077 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000035862 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_003246 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_003255 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000017, NC_018928 |
| UniProt ID(s) | A0A140VK57, P16035 |
| UniGene ID(s) | A0A140VK57, P16035 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 11821 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | TIMP2 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:7077 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA36527 |
| General Description of TIMP2. | |
| This MAb recognizes a protein of 21kDa, identified as tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2). It is closely related to TIMP-1 and shows the highest binding affinity to both the latent (pro) and active forms of 72kDa Type IV collagenase (also known as MMP-2 or gelatinase A). It also has affinity for the active form of 92kDa Type IV collagenase (also known as MMP-9 or gelatinase B). TIMP-2 inhibits the proteolytic invasiveness of tumor cells and normal placental trophoblast cells. | |




There are no reviews yet.