Human Anti-von Willebrand Factor Antibody Product Attributes
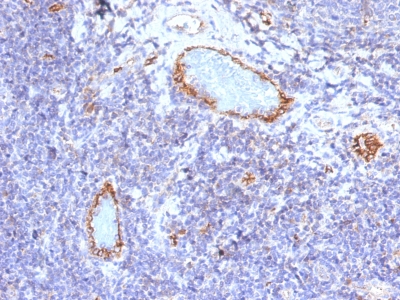
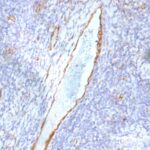
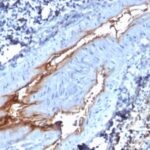
von Willebrand Factor Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in von Willebrand Factor antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex, colon. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex, colon. Low, but measureable presence of von Willebrand Factor could be seen infibroblasts in skin, keratinocytes in skin, Langerhans in skin, melanocytes in skin, adipocytes in mesenchymal tissue and fibroblasts in mesenchymal tissue. We were unable to detect von Willebrand Factor in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
| von Willebrand Factor General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Von Willebrand Factor, vWF | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 250kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 12p13.31 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | VWF |
| Entrez Gene ID | 7450 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000110799 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_000543 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_000552, |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000012, NC_018923, NG_009072 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P04275 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P04275 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 12726 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | VWF |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:7450 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA37337 |
| General Description of von Willebrand Factor. | |
| von Willebrand Factor (vWF) is a multimeric glycoprotein that is found in endothelial cells, plasma and platelets. It acts as a carrier protein for Factor VIII and promotes platelet adhesion and aggregation. vWF undergoes a variety of posttranslational modifications that influence the affinity and availability for Factor VIII, including cleavage of the propeptide and formation of N-terminal disulfide bonds. This antibody helps to establish the endothelial nature of some lesions of disputed histogenesis, e.g. Kaposi s sarcoma and cardiac myxoma. It is widely used for differentiating vascular lesions from those of other tissue differentiation within a panel of other vascular markers although not all tumors of endothelial differentiation contain this antigen. | |



There are no reviews yet.