Antibody DISCONTINUED
Application Notes
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:25-1:50 |
| Pretreatment | Citrate Buffer pH 6.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
Wilms Tumor 1 Protein , Information for Pathologists
Summary:
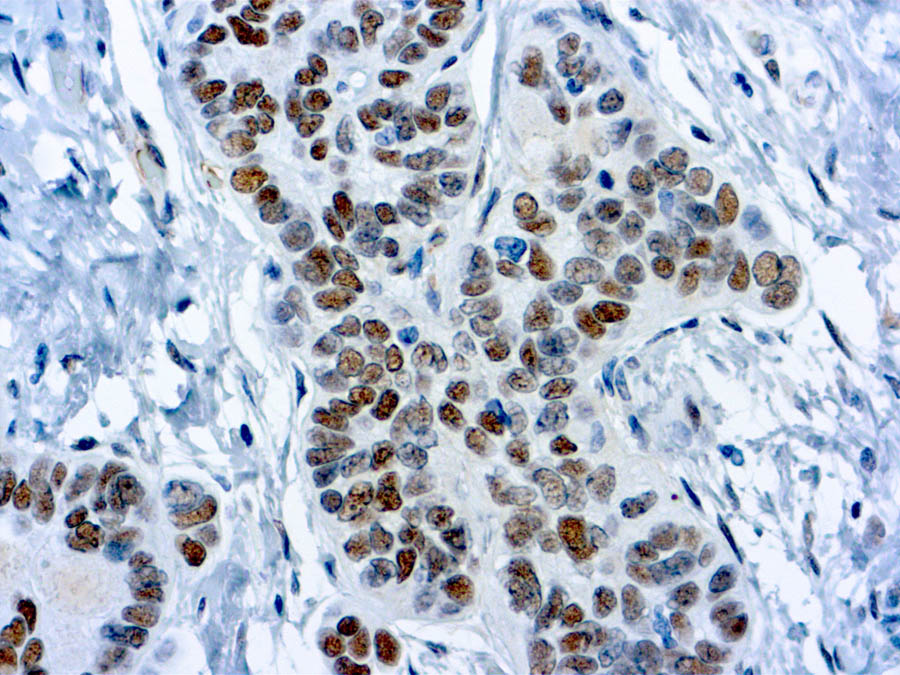
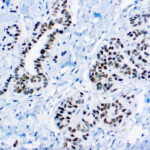
Tumor suppressor gene at 11p13. Protein is transcriptional regulator that apparently inhibits transcription of growth promoting genes. Involved in development of tissues from inner layer of intermediate mesoderm. Interpretation Nuclear stain.
Common Uses By Pathologists:
Ovarian carcinoma (WT1+) vs. breast/pancreatic carcinoma (WT1 negative). Positive staining – normal Fallopian tube, kidney, mesothelium, ovarian granulosa cells, Sertoli cells, spleen. Positive staining – disease Acute myeloid leukemia, cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma, desmoplastic small round cell tumor, malignant mesothelioma, metanephric adenoma, nephrogenic rests, ovarian carcinomas (serous carcinoma [almost all], transitional, small cell, Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1034), peritoneal serous carcinoma involving an endometrial polyp-80% (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1074), rhabdoid tumor, Wilm tumor.
| Wilms Tumor 1 Protein , General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 49.2 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| p13 [chr: 11] [chr_start: 32387775] [chr_end: 32435885] [strand: -1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | WT1 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 7490 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_077742; NP_001185481; NP_000369; NP_001185480; NP_077744 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_024426; NM_001367854; NM_024425; NM_001198551; NM_001198552; NM_024424; NM_000378; NR_160306 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000011; NG_009272; |
| UniProt ID(s) | P19544 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA37395 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:7490 |
| Associated Diseases (KEGG IDs) | Frasier syndrome (FS) [MIM:136680]: Characterized by a slowly progressing nephropathy leading to renal failure in adolescence or early adulthood, male pseudohermaphroditism, and no Wilms tumor. As for histological findings of the kidneys, focal glomerular sclerosis is often observed. There is phenotypic overlap with Denys-Drash syndrome. Inheritance is autosomal dominant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10571943}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Wilms tumor 1 (WT1) [MIM:194070]: Embryonal malignancy of the kidney that affects approximately 1 in 10’000 infants and young children. It occurs both in sporadic and hereditary forms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1317572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15150775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9108089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9529364}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Denys-Drash syndrome (DDS) [MIM:194080]: Typical nephropathy characterized by diffuse mesangial sclerosis, genital abnormalities, and/or Wilms tumor. There is phenotypic overlap with WAGR syndrome and Frasier syndrome. Inheritance is autosomal dominant, but most cases are sporadic. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10738002, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10799199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11182928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11519891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1302008, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1338906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15349765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1655284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8111391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8112732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8295405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8388765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8411073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8741319, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8956030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9475094, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9529364}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Nephrotic syndrome 4 (NPHS4) [MIM:256370]: A form of nephrotic syndrome, a renal disease clinically characterized by severe proteinuria, resulting in complications such as hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia and edema. Kidney biopsies show non-specific histologic changes such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and diffuse mesangial proliferation. Some affected individuals have an inherited steroid-resistant form and progress to end-stage renal failure. Most patients with NPHS4 show diffuse mesangial sclerosis on renal biopsy, which is a pathologic entity characterized by mesangial matrix expansion with no mesangial hypercellularity, hypertrophy of the podocytes, vacuolized podocytes, thickened basement membranes, and diminished patency of the capillary lumen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11182928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15253707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20798252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9529364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9607189}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Meacham syndrome (MEACHS) [MIM:608978]: Rare sporadically occurring multiple malformation syndrome characterized by male pseudohermaphroditism with abnormal internal female genitalia comprising a uterus and double or septate vagina, complex congenital heart defect and diaphragmatic abnormalities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17853480}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; A chromosomal aberration involving WT1 may be a cause of desmoplastic small round cell tumor (DSRCT). Translocation t(11;22)(p13;q12) with EWSR1.; Mesothelioma, malignant (MESOM) [MIM:156240]: An aggressive neoplasm of the serosal lining of the chest. It appears as broad sheets of cells, with some regions containing spindle-shaped, sarcoma-like cells and other regions showing adenomatous patterns. Pleural mesotheliomas have been linked to exposure to asbestos. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8401592}. The disease may be caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| General Description of Wilms Tumor 1 Protein , . | |
| Wilms’ Tumor (WT1) is a gene involved in the induction of Wilms’ tumor, a pediatric renal malignancy that is associated with mutations of WT1, a zinc-finger transcription factor that is essential for the development of the metanephric kidney and the urogenital system. The WT1 gene is normally expressed in fetal kidney and mesothelium and its expression has been suggested as a marker for Wilms’ tumor and mesothelioma. | |



There are no reviews yet.