Human Anti-Bcl-6 (Follicular Lymphoma Marker) Antibody Product Attributes
Bcl-6 (Follicular Lymphoma Marker) Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-BCL6 antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the nucleoplasm.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in Bcl-6 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow and respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and nasopharynx. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow and respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus and nasopharynx. Low, but measureable presence of Bcl-6 could be seen in cells in the red pulp in spleen, epidermal cells in the skin, fibroblasts in mesenchymal tissue, glandular cells in the appendix, epididymis, rectum and stomach, keratinocytes in skin, Leydig cells in the testis, myocytes in skeletal muscle, neuronal cells in the cerebral cortex, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil, peripheral nerve in mesenchymal tissue, Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, squamous epithelial cells in the oral mucosa and trophoblastic cells in the placenta. We were unable to detect Bcl-6 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of Bcl-6 expression as measured by anti-Bcl-6 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – |
| BCL6 Variability | + | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | + | +++ | + | + | + |
| Bcl-6 (Follicular Lymphoma Marker) General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| B-cell lymphoma 5 protein; B-Cell Lymphoma 6 Protein; BCL5; BCL6; BCL6A; cys his2 zinc finger transcription factor; Lymphoma Associated Zinc Finger Gene On Chromosome 3 (LAZ3); Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 27 (ZBTB27); Zinc Finger Protein 51 (ZNF51); zinc finger transcription factor BCL6S | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 95kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| Ships on blue ice. | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | 604 |
| Entrez Gene ID | BCL6 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P41182 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs478588 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | BCL6 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:604 |
| General Description of Bcl-6 (Follicular Lymphoma Marker). | |
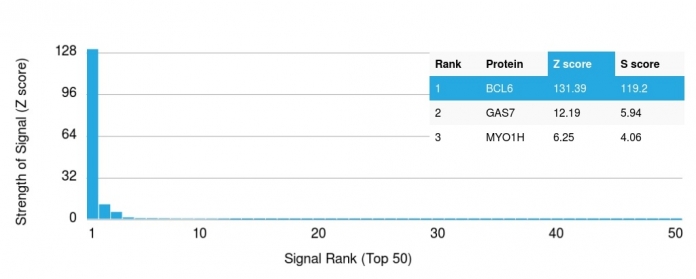
| The specificity of this monoclonal antibody to its intended target was validated by HuProtTM Array, containing more than 19,000, full-length human proteins. Recognizes a protein of 95kDa, which is identified as Bcl-6. Antibody to bcl-6 is helpful in a number of diagnostic settings: (1) In the differential diagnosis of small B-cell lymphoma. Follicular lymphoma will show bcl-6 (and CD10) positivity whereas other small B-cell lymphomas are usually negative. (2) Bcl-6 is an important prognostic marker in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL), where CD10, bcl-6 and MUM1/IRF4 are used to identify germinal center and activated B-cell phenotypes. (3) Bcl-6 can be valuable in distinguishing classical Hodgkin lymphoma from nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL). The Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma are bcl-6 negative whereas the large ( L&H ) cells of NLPHL are bcl-6 positive. In contrast, anti-Bcl-6 rarely stains mantle-cell lymphoma and MALT lymphoma. | |

.jpg)

.jpg)
%20Gel.jpg)

There are no reviews yet.