Human Anti-NGF-Receptor (p75) / CD271 (Soft Tissue Tumor Marker) Antibody Product Attributes
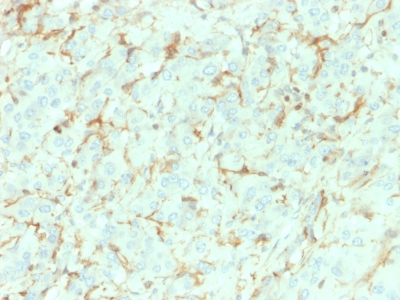
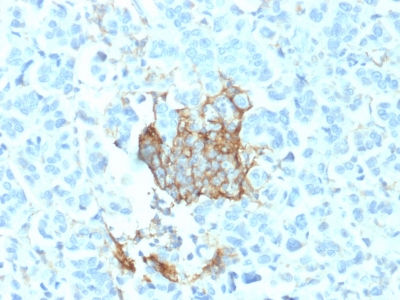
NGF-Receptor (p75) / CD271 (Soft Tissue Tumor Marker) Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-NGFR antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the nucleoplasm and plasma membrane.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in NGF-Receptor / CD271 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in peripheral nerve/ganglion in colon. Low, but measureable presence of NGF-Receptor / CD271 could be seen inrespiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine and esophagus, glandular cells in the gallbladder, respiratory epithelial cells in the nasopharynx, squamous epithelial cells in the oral mucosa, keratinocytes in skin and squamous epithelial cells in the tonsil. We were unable to detect NGF-Receptor / CD271 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
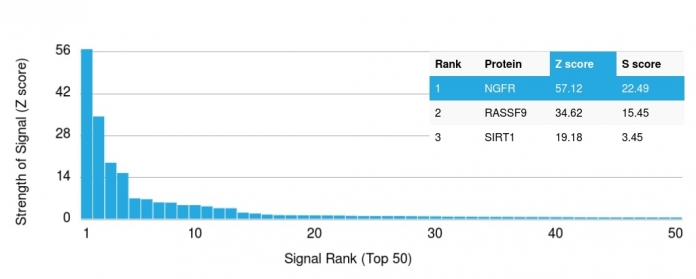
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of NGF-Receptor / CD271 expression as measured by anti-NGF-Receptor / CD271 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| NGFR Variability | + | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | ++ |
| NGF-Receptor (p75) / CD271 (Soft Tissue Tumor Marker) General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| CD271; Gp80-LNGFR; Low affinity nerve growth factor receptor; Low affinity neurotrophin receptor p75NTR; Nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR); p75 ICD; p75 Neurotrophin receptor; Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 16 (TNFRSF16) | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 75kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| Ships on blue ice. | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | 4804 |
| Entrez Gene ID | NGFR |
| UniProt ID(s) | P08138 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs415768 & 681726 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | NGFR |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:4804 |
| General Description of NGF-Receptor (p75) / CD271 (Soft Tissue Tumor Marker). | |
| It recognizes a glycoprotein of 75kDa, identified as low affinity Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Receptor (p75NGFR) or Neurotrophin Receptor (p75NTR). NGFR is expressed in various neural crest cells and their tumors such as melanocytes, melanomas, neuroblastomas, pheochromocytomas and neurofibromas. Reportedly, anti-NGFR is a reliable marker for desmoplastic and neurotropic melanomas. NGFR is expressed in mature non-neural cells such as perivascular cells, dental pulp cells, lymphoidal follicular dendritic cells, basal epithelium of oral mucosa and hair follicles, prostate basal cells, and myoepithelial cells. Anti-NGFR stains the myoepithelial cells of breast ducts and intra-lobular fibroblasts of breast ducts. | |





There are no reviews yet.