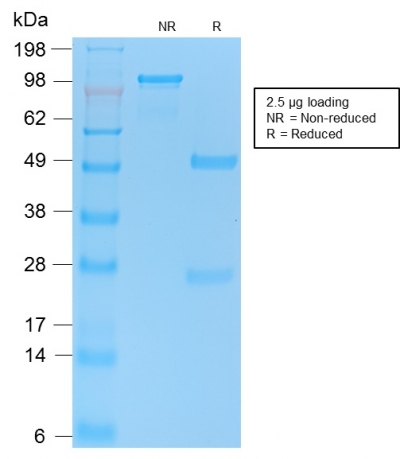
Human, Monkey, Dog, Hamster and Chicken. Does not react with mouse and rat. Anti-p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein Antibody Product Attributes
p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
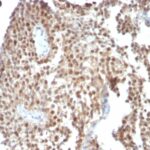
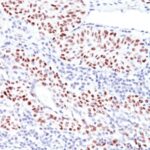
Variations in p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. Low, but measureable presence of p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein could be seen inglandular cells in the adrenal gland, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, glandular cells in the breast, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, neuronal cells in the caudate nucleus, glandular cells in the cervix, uterine and endometrium, cells in the glomeruli in kidney, islets of Langerhans in pancreas, glandular cells in the parathyroid gland, decidual cells in the placenta, glandular cells in the salivary gland, fibroblasts in skin, cells in the white pulp in spleen, non-germinal center cells in the tonsil and squamous epithelial cells in the vagina. We were unable to detect p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein expression as measured by anti-p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | + | + | – | – | – | – | + | – | + | – | ++ | – | – | + | + | + | – | ++ |
| TP53 Variability | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | +++ |
| p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Antigen NY-CO-13, BCC7, Cellular Tumor Antigen p53, LFS1, TP53, Transformation Related Protein 53 (TRP53), Tumor Protein p53, Tumor Suppressor p53 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
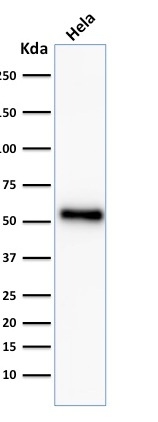
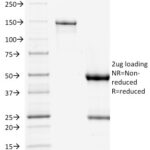
| 53kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| Ships on blue ice. | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | 7157 |
| Entrez Gene ID | TP53 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P04637 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs654481 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | TP53 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:7157 |
| General Description of p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein. | |
| This MAb reacts with an N-terminal epitope (aa 16-25) of both wild type and mutated p53. Mutation and/or allelic loss of p53 is one of the causes of a variety of mesenchymal and epithelial tumors. If it occurs in the germ line, such tumors run in families. In most transformed and tumor cells the concentration of p53 is increased 51000 fold over the minute concentrations (1000 molecules cell) in normal cells, principally due to the increased half-life (4 h) compared to that of the wild-type (20 min). p53 Localizes in the nucleus, but is detectable at the plasma membrane during mitosis and when certain mutations modulate cytoplasmic/nuclear distribution. Mutations arise with an average frequency of 70% but incidence varies from zero in carcinoid lung tumors to 97% in primary melanomas. High concentrations of p53 protein are transiently expressed in human epidermis and superficial dermal fibroblasts following mild ultraviolet irradiation. Positive nuclear staining with p53 antibody has been reported to be a negative prognostic factor in breast carcinoma, lung carcinoma, colorectal, and urothelial carcinoma. Anti-p53 positivity has also been used to differentiate uterine serous carcinoma from endometrioid carcinoma as well as to detect intratubular germ cell neoplasia. | |


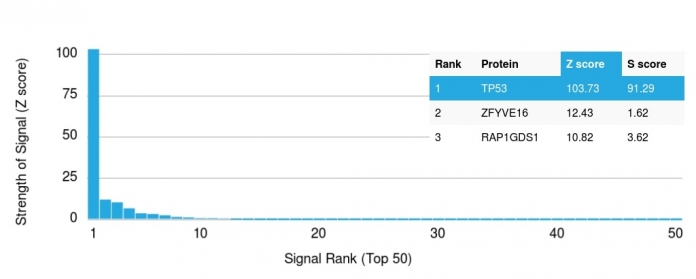
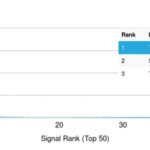
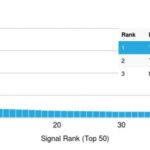
![Analysis of Mass Spec data (dashed-line) of fractions stained with p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein <a href="https://enquirebio.com/validation-project-details/" target="_blank">MS-QAVA™ monoclonal antibody</a> [Clone: DO-7] (solid-line), reveals that less than 12.1% of signal is attributable to non-specific binding of anti-p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein [Clone DO-7] to targets other than TP53 protein. Even frequently cited antibodies have much greater non-specific interactions, averaging over 30%. Data in image is from analysis in A431, RT4 and MCF7 cells.](https://cdn-enquirebio.pressidium.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/enQuire-Bio-7157-MSM2-P1-anti-p53-Tumor-Suppressor-Protein-antibody-150x150.png)
-150x150.jpg)
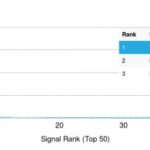
![Analysis of Mass Spec data (dashed-line) of fractions stained with p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein <a href="https://enquirebio.com/validation-project-details/" target="_blank">MS-QAVA™ monoclonal antibody</a> [Clone: BP53-12] (solid-line), reveals that less than 12.9% of signal is attributable to non-specific binding of anti-p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein [Clone BP53-12] to targets other than TP53 protein. Even frequently cited antibodies have much greater non-specific interactions, averaging over 30%. Data in image is from analysis in A431, RT4 and MCF7 cells.](https://cdn-enquirebio.pressidium.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/enQuire-Bio-7157-MSM1-P1-anti-p53-Tumor-Suppressor-Protein-antibody-150x150.png)
![Analysis of Mass Spec data (dashed-line) of fractions stained with p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein <a href="https://enquirebio.com/validation-project-details/" target="_blank">MS-QAVA™ monoclonal antibody</a> [Clone: BP53-12 + DO-7] (solid-line), reveals that less than 10.8% of signal is attributable to non-specific binding of anti-p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein [Clone BP53-12 + DO-7] to targets other than TP53 protein. Even frequently cited antibodies have much greater non-specific interactions, averaging over 30%. Data in image is from analysis in A431, RT4 and MCF7 cells.](https://cdn-enquirebio.pressidium.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/enQuire-Bio-7157-MSM3-P1-anti-p53-Tumor-Suppressor-Protein-antibody-150x150.png)

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.