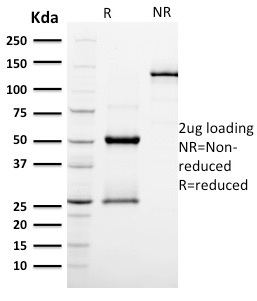
Human Anti-Podocalyxin (PODXL) (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Marker) Antibody Product Attributes
Podocalyxin (PODXL) (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Marker) Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
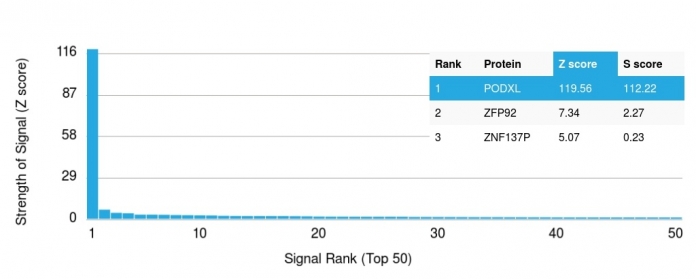
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-PODXL antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the plasma membrane, microtubule organizing center and vesicles.
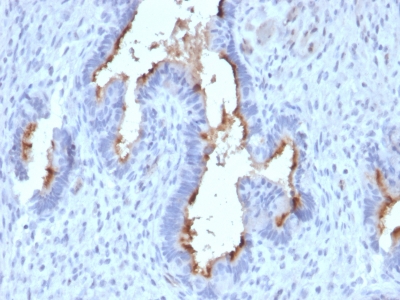
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in Podocalyxin antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex, glandular cells in the fallopian tube and cells in the glomeruli in kidney. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex, glandular cells in the fallopian tube and cells in the glomeruli in kidney. Low, but measureable presence of Podocalyxin could be seen inglandular cells in the breast, decidual cells in the placenta and glandular cells in the seminal vesicle. We were unable to detect Podocalyxin in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of Podocalyxin expression as measured by anti-Podocalyxin antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | – | – | ++ | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| PODXL Variability | + | + | + | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | + |
| Podocalyxin (PODXL) (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Marker) General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| PODXL, PDXL, GCTM-2; Gp200; PCLP1; Pcx; Podocalyxin-like protein 1 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 165-170kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| Ships on blue ice. | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | 5420 |
| Entrez Gene ID | PODXL |
| UniProt ID(s) | O00592 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs732423 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | PODXL |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:5420 |
| General Description of Podocalyxin (PODXL) (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Marker). | |
| Podocalyxin is a member of the CD34 transmembrane sialomucin family. It is over-expressed on the podocyte foot projections and plays essential roles in kidney development and homeostasis, blood filtration and urine formation. It is also expressed on vascular endothelia, hematopoietic progenitors and a subset of neurons. Overexpression of podocalyxin may be linked to more aggressive tumor behavior. Podocalyxin antibody can identify podocytes in the urine (podocyturia) that may indicate glomerular disease, pre-eclampsia, and other kidney pathology. | |



There are no reviews yet.