Human Anti-Alkaline Phosphatase Antibody Product Attributes
Alkaline Phosphatase Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
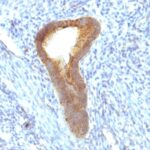
Anti-ALPI antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the plasma membrane.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in Alkaline Phosphatase antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in glandular cells in the duodenum, small intestine. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in glandular cells in the duodenum, small intestine. Low, but measureable presence of Alkaline Phosphatase could be seen in. We were unable to detect Alkaline Phosphatase in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of Alkaline Phosphatase expression as measured by anti-Alkaline Phosphatase antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| ALPI Variability | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | + |
| Alkaline Phosphatase General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Alkaline phosphatase, Intestinal ALPI, ALPI | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 55kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 2q37.1 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | ALPI |
| Entrez Gene ID | 248 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000163295 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001622 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001631 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000002, NC_018913 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P09923, A0A024R4A2 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P09923, A0A024R4A2 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 437 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | ALPI |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:248 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA24728 |
| General Description of Alkaline Phosphatase. | |
| There are at least four distinct but related alkaline phosphatases: intestinal, placental, placental-like,, liver/bone/kidney (tissue non-specific). The first three are located together on chromosome 2, while the tissue non-specific form is located on chromosome 1. The product of this gene is a membrane bound glycosylated enzyme that is not expressed in any particular tissue, is, therefore, referred to as the tissue-nonspecific form of the enzyme. The exact physiological function of the alkaline phosphatases is not known. A proposed function of this form of the enzyme is matrix mineralization; however, mice that lack a functional form of this enzyme show normal skeletal development. This enzyme has been linked directly to hypo-phosphatasia, a disorder that is characterized by hypercalcemia, includes skeletal defects. The character of this disorder can vary, however, depending on the specific mutation since this determines age of onset, severity of symptoms. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, which encode the same protein, have been identified for this gene. | |





There are no reviews yet.