Human Anti-CD79a Antibody Product Attributes
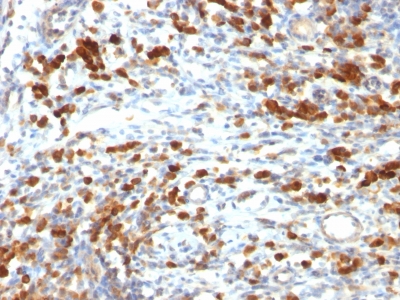
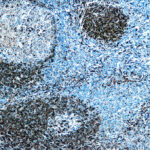
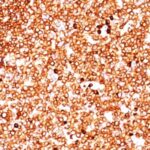
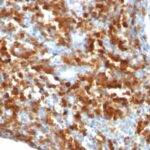
CD79a Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
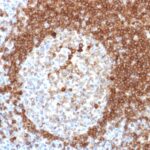
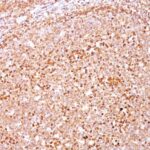
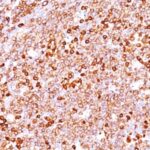
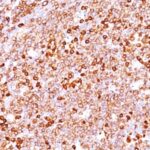
Variations in CD79a antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in cells in the white pulp in spleen, germinal center cells in the lymph node, lymphoid tissue in appendix and non-germinal center cells in the tonsil. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in cells in the white pulp in spleen, germinal center cells in the lymph node, lymphoid tissue in appendix and non-germinal center cells in the tonsil. Low, but measureable presence of CD79a could be seen inmacrophages in lung. We were unable to detect CD79a in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
| CD79a General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Cluster of differentiation CD79A, B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein alpha chain, MB-1 membrane glycoprotein, CD79A | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 44kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 19q13.2 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | CD79A |
| Entrez Gene ID | 973 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000105369 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001774, NP_067612 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_021601, NM_001783, |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_009619, NC_018930, NC_000019 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P11912 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P11912 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 1698 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | CD79A |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:973 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA26237 |
| General Description of CD79a. | |
| A disulphide-linked heterodimer, consisting of mb-1 (or CD79a), B29 (or CD79b) polypeptides, is non-covalently associated with membrane-bound immunoglobulins on B cells. This complex of mb-1, B29 polypeptides, immunoglobulin constitute the B cell Ag receptor. CD79a first appears at pre B cell stage, early in maturation,, persists until the plasma cell stage where it is found as an intracellular component. CD79a is found in the majority of acute leukemias of precursor B cell type, in B cell lines, B cell lymphomas,, in some myelomas. It is not present in myeloid or T cell lines. Anti-CD79a is generally used to complement anti-CD20 especially for mature B-cell lymphomas after treatment with Rituximab (anti-CD20). This antibody will stain many of the same lymphomas as anti-CD20, but also is more likely to stain B-lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia than is anti-CD20. Anti-CD79a also stains more cases of plasma cell myeloma, occasionally some types of endothelial cells as well. | |






There are no reviews yet.