Human and Rat Anti-Cytochrome C Antibody Product Attributes
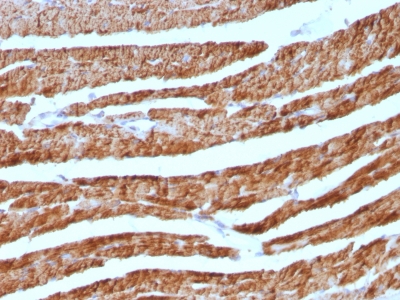
Cytochrome C Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-CYCS antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the mitochondria.
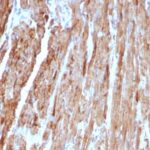
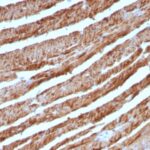
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in Cytochrome C antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, cells in the tubules in kidney, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, glandular cells in the appendix, breast, colon, duodenum, gallbladder, parathyroid gland, prostate, rectum, salivary gland, seminal vesicle, small intestine and stomach, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, islets of Langerhans in pancreas, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, trophoblastic cells in the placenta and urothelial cells in the urinary bladder. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in cells in the seminiferous ducts in testis, cells in the tubules in kidney, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, glandular cells in the appendix, breast, colon, duodenum, gallbladder, parathyroid gland, prostate, rectum, salivary gland, seminal vesicle, small intestine and stomach, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, islets of Langerhans in pancreas, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node, trophoblastic cells in the placenta and urothelial cells in the urinary bladder. Low, but measureable presence of Cytochrome C could be seen inadipocytes in breast and mesenchymal tissue, bile duct cells in the liver, cells in the endometrial stroma in endometrium, cells in the red pulp in spleen, cells in the white pulp in spleen, chondrocytes in mesenchymal tissue, endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex and colon, fibroblasts in skin and mesenchymal tissue, follicle cells in the ovary, glial cells in the caudate nucleus, cerebral cortex and hippocampus, melanocytes in skin, neuropil in cerebral cortex, ovarian stroma cells in the ovary, peripheral nerve in mesenchymal tissue and pneumocytes in lung. We were unable to detect Cytochrome C in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
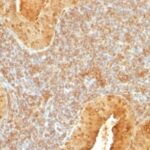
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of Cytochrome C expression as measured by anti-Cytochrome C antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| CYCS Variability | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | ++ |
| Cytochrome C General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Cytochrome C, Cytochrome Complex, CYCS | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 15kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 7p15.3 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | CYCS |
| Entrez Gene ID | 54205 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000172115 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_061820 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_018947 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_023438, NC_000007, NC_018918 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P99999, Q96BV4, P00001, G4XXL9 |
| UniGene ID(s) | P99999, Q96BV4, P00001, G4XXL9 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 19986 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | CYCS |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:54205 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA134981636 |
| General Description of Cytochrome C. | |
| Cytochrome C is a well-characterized mobile electron transport protein that is essential to energy conversion in all aerobic organisms. In mammalian cells, this highly conserved protein is normally localized to the mitochondrial inter-membrane space. More recent studies have identified cytosolic cytochrome c as a factor necessary for activation of apoptosis. During apoptosis, cytochrome c is trans-located from the mitochondrial membrane to the cytosol, where it is required for activation of caspase-3 (CPP32). Overexpression of Bcl-2 has been shown to prevent the translocation of cytochrome c, thereby blocking the apoptotic process. Overexpression of Bax has been shown to induce the release of cytochrome c, to induce cell death. The release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria is thought to trigger an apoptotic cascade, whereby Apaf-1 binds to Apaf-3 (caspase-9) in a cytochrome c-dependent manner, leading to caspase-9 cleavage of caspase-3. This MAb recognizes total cytochrome C which includes both apocytochrome (i.e. cytochrome in the cytosol without heme attached), holocytochrome (i.e cytochrome in the mitochondria with heme attached). | |



There are no reviews yet.