Antibody (Suitable for clinical applications)
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:25-1:50 |
| Pretreatment | Citrate Buffer pH 6.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
Cytokeratin 10 Information for Pathologists
Summary:
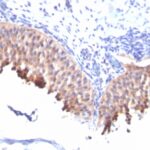
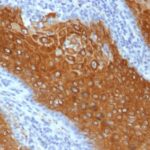
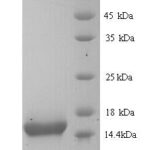
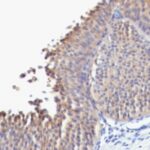
Molecular weight of 56.5 kDa. Partner of CK1. CK1 and CK10 are present in suprabasal terminally differentiating cells. Mutations in CK10 or CK1 cause epidermolytic hyperkeratosis / bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma of Brocq (Hum Mol Genet 2006;15:1133, Dermatol Online J 2006;12:6); defects of CK10-CK1 protein network cause structural instability and weakness of keratinocytes, causing blistering, hyperproliferation and hyperkeratosis. CK10 is putative autoantigen in chronic, antibiotic resistant Lyme arthritis (J Immunol 2006;177:2486).
Common Uses By Pathologists:
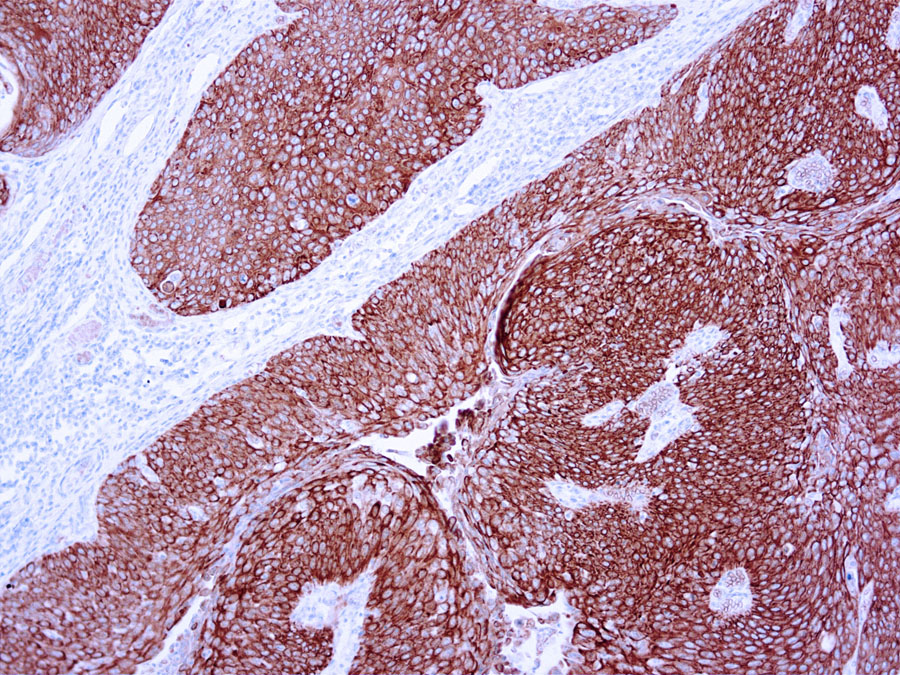
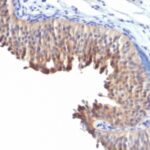
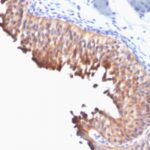
Helps distinguish inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (higher CK10) from psoriasis (Eur J Dermatol 2004;14:216). Increase indicates a response to treatment for psoriasis (J Am Acad Dermatol 2004;51:257). Positive staining – normal Epidermal spinous and granular cell layers. Positive staining – disease
| Cytokeratin 10 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 58.8 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| q21.2 [chr: 17] [chr_start: 40818117] [chr_end: 40822614] [strand: -1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | KRT10 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 3858 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_000412 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | ; NM_000421; XM_005257343 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_008405; NC_000017 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P13645 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA30200 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:3858 |
| Associated Diseases (KEGG IDs) | Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (EHK) [MIM:113800]: An autosomal dominant skin disorder characterized by widespread blistering and an ichthyotic erythroderma at birth that persist into adulthood. Histologically there is a diffuse epidermolytic degeneration in the lower spinous layer of the epidermis. Within a few weeks from birth, erythroderma and blister formation diminish and hyperkeratoses develop. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10201536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1380725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1381287, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21271994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7507150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7507152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7508181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7512983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7526210, ECO:0000269|Ref.7}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Ichthyosis annular epidermolytic (AEI) [MIM:607602]: A skin disorder resembling bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma. Affected individuals present with bullous ichthyosis in early childhood and hyperkeratotic lichenified plaques in the flexural areas and extensor surfaces at later ages. The feature that distinguishes AEI from BCIE is dramatic episodes of flares of annular polycyclic plaques with scale, which coalesce to involve most of the body surface and can persist for several weeks or even months. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9036939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9856845}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Erythroderma, ichthyosiform, congenital reticular (CRIE) [MIM:609165]: A rare skin condition characterized by slowly enlarging islands of normal skin surrounded by erythematous ichthyotic patches in a reticulated pattern. The condition starts in infancy as a lamellar ichthyosis, with small islands of normal skin resembling confetti appearing in late childhood and at puberty. Histopathologic findings include band-like parakeratosis, psoriasiform acanthosis, and vacuolization of keratinocytes with binucleated cells in the upper epidermis, sometimes associated with amyloid deposition in the dermis. Ultrastructural abnormalities include perinuclear shells formed from a network of fine filaments in the upper epidermis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20798280}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| General Description of Cytokeratin 10 . | |
| This antibody recognizes keratin polypeptide of 56.5 kDa. It stains suprabasal cells in the epidermis, thymic Hassall’s bodies. Simple and glandular epithelia, transitional epithelium and adenocarcinomas are negative with this antibody. | |




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.