Antibody (Suitable for clinical applications)
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:50-1:200 |
| Pretreatment | Citrate Buffer pH 6.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
Cytokeratin 14 Information for Pathologists
Summary:
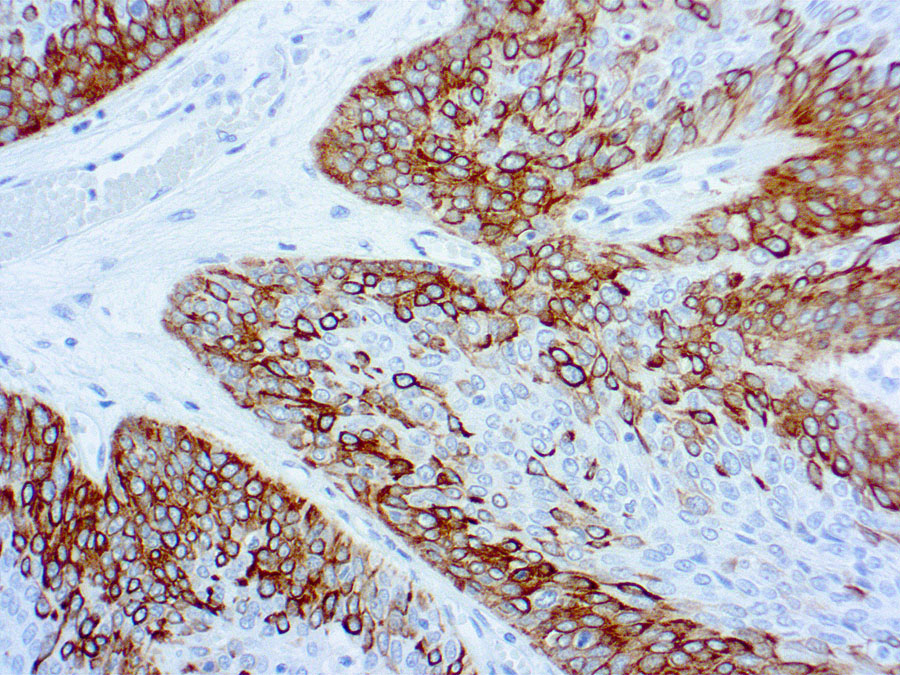
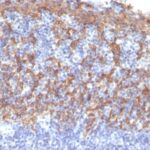
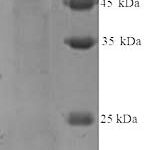
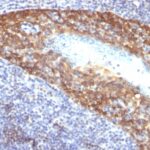
Molecular weight of 50 kDa. Partner is CK5. May be detected by cytokeratin 34BE12. CK5/6+ or CK14+ tumors define a basal subtype of DCIS (Mod Pathol 2006;19:1506) or invasive breast carcinoma; represents 9% of sporadic invasive ductal breast cancers, ER-, PR-, HER2-, high grade, poor prognosis (Mod Pathol 2005;18:1321, Eur J Cancer 2006;42:3149 but see Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:5988-not poor prognosis), associated with BRCA1 (Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:5175). In cervix, loss of expression is associated with high grade SIL and high risk HPV (Hum Pathol 2001;32:1351).
Common Uses By Pathologists:
Distinguish parathyroid oxyphil adenoma (CK14+) from carcinoma (CK14-, Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:344). Distinguish breast papilloma (stronger and more diffuse CK14 staining) from papillary DCIS (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:625). Distinguish sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma (poorly differentiated or nonkeratinizing, both CK14+) from sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma or nasopharyngeal carcinoma (CK14-, Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1597). Positive staining – normal Basal keratinocytes in stratified epithelium (various tissue/organs).
| Cytokeratin 14 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 51.6 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| q21.2 [chr: 17] [chr_start: 41582279] [chr_end: 41586895] [strand: -1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | KRT14 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 3861 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_000517 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | ; NM_000526 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_008624; NC_000017 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P02533 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA30203 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:3861 |
| Associated Diseases (KEGG IDs) | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Dowling-Meara type (DM-EBS) [MIM:131760]: A severe form of intraepidermal epidermolysis bullosa characterized by generalized herpetiform blistering, milia formation, dystrophic nails, and mucous membrane involvement. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10583131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10730767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10733662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10820403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11710919, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12603865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14987259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1717157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7561171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7688405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8601736, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794, ECO:0000269|Ref.32}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Weber-Cockayne type (WC-EBS) [MIM:131800]: A form of intraepidermal epidermolysis bullosa characterized by blistering limited to palmar and plantar areas of the skin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10733662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12603865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12655565, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14987259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7506097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7506606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7561171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9284105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Koebner type (K-EBS) [MIM:131900]: A form of intraepidermal epidermolysis bullosa characterized by generalized skin blistering. The phenotype is not fundamentally distinct from the Dowling-Meara type, although it is less severe. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10733662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10820403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11710919, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16786515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1720261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7526926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7682883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9989794, ECO:0000269|Ref.10, ECO:0000269|Ref.32}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, autosomal recessive 1 (EBSB1) [MIM:601001]: A form of epidermolysis bullosa, a genodermatosis characterized by recurrent blistering and cleavage within basal keratinocytes, fragility of the skin and mucosal epithelia, and erosions caused by minor mechanical trauma. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7526933}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome (NFJS) [MIM:161000]: A rare autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia. The cardinal features are absence of dermatoglyphics (fingerprints), reticular cutaneous hyperpigmentation (starting at about the age of 2 years without a preceding inflammatory stage), palmoplantar keratoderma, hypohidrosis with diminished sweat gland function and discomfort provoked by heat, nail dystrophy, and tooth enamel defects. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16960809}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.; Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis (DPR) [MIM:125595]: A rare ectodermal dysplasia characterized by lifelong persistent reticulate hyperpigmentation, non-cicatricial alopecia, and nail dystrophy. Variable features include adermatoglyphia, hypohidrosis or hyperhidrosis, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16960809}. The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| General Description of Cytokeratin 14 . | |
| This antibody is specific to 50 kDa cytokeratin protein designated cytokeratin 14. Cytokeratin 14 belongs to the type A (acidic) subfamily of low molecular weight cytokeratins and exists in combination with cytokeratin 15. This antibody can be used to distinguish stratified epithelial cells from simple epithelial cells. | |




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.