Human, Monkey, and Mouse (-) Anti-HLA-DRB Antibody Product Attributes
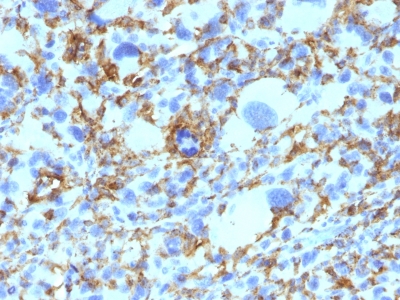
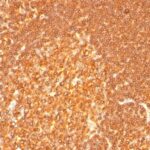
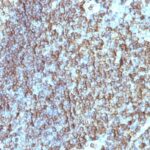
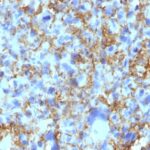
HLA-DRB Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
Variations in HLA-DRB antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil, macrophages in lung and non-germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil, macrophages in lung and non-germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil. Low, but measureable presence of HLA-DRB could be seen in cells in the red pulp in spleen, cells in the white pulp in spleen and pneumocytes in lung. We were unable to detect HLA-DRB in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of HLA-DRB expression as measured by anti-HLA-DRB antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ++ | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| HLA-DRB1 Variability | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| HLA-DRB General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain, HLA-DRB1 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 28kDa (beta chain) | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 6p21.3 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | HLA-DRB1 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 3123 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000206240, ENSG00000236884, ENSG00000206306, ENSG00000228080, ENSG00000229074, ENSG00000196126 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | XP_011546040, NP_001230894, NP_002115 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001243965, XM_011547738, NM_002124 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_029921, NG_002392, NG_167248, NC_018917, NG_002433, NC_000006, NG_002432, NG_113891, NG_167245, NG_167249, NG_167246 |
| UniProt ID(s) | Q29974, D7RIG5, P01912, X5DNQ0, D7RIH8, Q5Y7D1, P13761, P01911 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Q29974, D7RIG5, P01912, X5DNQ0, D7RIH8, Q5Y7D1, P13761, P01911 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 4948 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | HLA-DRB1 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:3123 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA35072 |
| General Description of HLA-DRB. | |
| This MAb reacts with a 28kDa chain of HLA-DRB1 antigen, a member of MHC class II molecules. It does not cross react with HLA-DP, HLA-DQ. The L243 antibody recognizes a different epitope than the LN3 monoclonal antibody,, these antibodies do not cross-block binding to each other’s respective epitopes. HLA-DR is a heterodimeric cell surface glycoprotein comprised of a 36kDa alpha (heavy) chain, a 28kDa beta (light) chain. It is expressed on B-cells, activated T-cells, monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, other non-professional APCs. In conjunction with the CD3/TCR complex, CD4 molecules, HLA-DR is critical for efficient peptide presentation to CD4+ T cells. It is an excellent histiocytic marker in paraffin sections producing intense staining. True histiocytic neoplasms are similarly positive. HLA-DR antigens also occur on a variety of epithelial cells, their corresponding neoplastic counterparts. Loss of HLA-DR expression is related to tumor microenvironment, predicts adverse outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. | |





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.