Antibody (Suitable for clinical applications)
| Specification | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution (Conc) | 1:50-1:100 |
| Pretreatment | Citrate Buffer pH 6.0 |
| Incubation Parameters | 30 min at Room Temperature |
Prior to use, inspect vial for the presence of any precipitate or other unusual physical properties. These can indicate that the antibody has degraded and is no longer suitable for patient samples. Please run positive and negative controls simultaneously with all patient samples to account and control for errors in laboratory procedure. Use of methods or materials not recommended by enQuire Bio including change to dilution range and detection system should be routinely validated by the user.
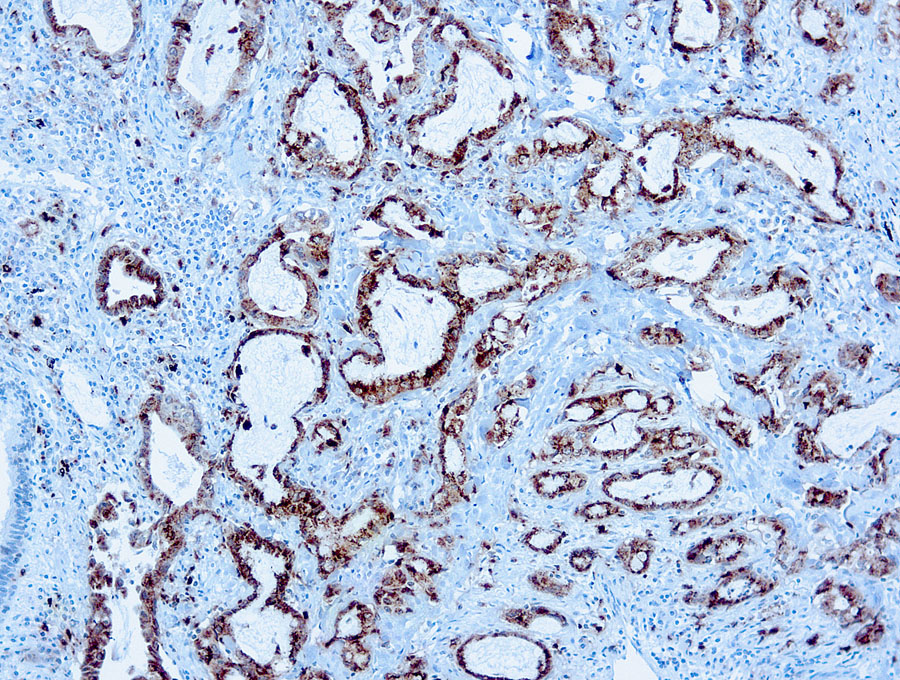
Napsin A Information for Pathologists
Summary:
A novel aspartic proteinase of the pepsin family involved in the maturation of surfactant protein B. Found primarily in lung and kidney. Lack of NapsinA expression in tumor cells may be poor prognostic marker in pulmonary adenocarcinoma (Lung Cancer 2012;77:156). Uses by pathologists Useful individually (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:396) or as part of panel (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:155, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:350) to distinguish lung adenocarcinoma (positive) from squamous cell carcinoma (negative in tumor cells but positive in hyperplastic type II pneumocytes and intra-alveolar macrophages entrapped within tumor cells).
Common Uses By Pathologists:
Useful individually (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:396) or as part of panel (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:155, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:350) to distinguish lung adenocarcinoma (positive) from squamous cell carcinoma (negative in tumor cells but positive in hyperplastic type II pneumocytes and intra-alveolar macrophages entrapped within tumor cells). Useful as part of panel to classify poorly differentiated non small cell lung carcinoma on small biopsies (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:15), fine needle aspirates (Cytojournal 2012;9:10) or bronchial brushings (Cancer Cytopathol 2011;119:335). Superior to TTF1 in distinguishing primary lung adenocarcinoma from other carcinomas (except kidney), particularly primary lung small cell carcinoma and primary thyroid carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:163). Superior to TTF1 in distinguishing metastatic pulmonary (positive) from nonpulmonary (negative) adenocarcinoma in cell blocks prepared from malignant pleural effusions (Acta Cytol 2011;55:266) or from fine needle aspirates (Cancer Cytopathol 2011;119:127). May help identify metastatic disease with unknown primary as originating in lung (Case Rep Oncol 2011;4:564).
| Napsin A General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 45.4 kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| q13.33 [chr: 19] [chr_start: 50358477] [chr_end: 50365830] [strand: -1] | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | NAPSA |
| Entrez Gene ID | 9476 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_004842; XP_011525842 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_004851; XM_011527540; XM_017027512 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NC_000019 |
| UniProt ID(s) | O96009 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA134891814 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:9476 |
| General Description of Napsin A . | |
| Napsin is found in two isoforms, A and B, with highly homologous gene sequences. Napsin A has a molecular weight of 35.0 kDa and is also known as TA02. Napsin A is an aspartic proteinase which is expressed in the lung and involved in processing surfactant protein B (SP-B). It is also expressed in the kidney. This antibody may be a useful tool as a tumor marker for primary lung adenocarcinoma. Napsin expression correlates with the differentiation grade of lung adenocarcinoma. | |


-150x150.jpg)
-150x150.jpg)
-150x150.jpg)

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.