Human ATP5D Recombinant Protein Product Attributes
Product Type: Recombinant Protein
Recombinant ATP5D based upon sequence from Human
Host: QP5695 protein expressed in E.coli, Yeast..
Tag: His-SUMO
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the Homo sapiens (Human) ATP5D, was expressed in the hosts and tags indicated. Please select your host/tag option, above.
Recommended Applications: Immunogen, Protein Standard, Cell culture, or Other Cell Biology Applications.
Application Notes: Please contact us for application specific information for QP5695.
Bioactivity Data: Untested
Full Length? Full Length
Expression Region: Ala23 – Glu168
Amino Acid Sequence: AEAAAAPAAA SGPNQMSFTF ASPTQVFFNG ANVRQVDVPT LTGAFGILAA HVPTLQVLRP GLVVVHAEDG TTSKYFVSSG SIAVNADSSV QLLAEEAVTL DMLDLGAAKA NLEKAQAELV GTADEATRAE IQIRIEANEA LVKALE
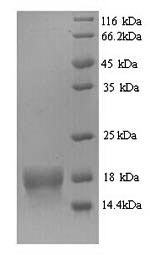
Purity: Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Reconstitution Instructions: Concentrated protein in liquid format. Reconstitution is not necessary.
Concentration of Human ATP5D Protein:
Endotoxin Levels: Not determined.
Buffer: Tris-based buffer, 50% glycerol
Storage Conditions: Store at -20C to -80C.
| Recombinant Human ATP5D Protein General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| ATP5D | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | ATP5D |
| Entrez Gene ID | 513 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000099624 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001001975.1 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001001975.1, NM_001687.4 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P30049 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs.418668 |
| HGNC ID(s) | HGNC:837 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | ATP5D |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:513 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA25127 |
| General Description of Recombinant Human ATP5D Protein. | |
| Mitochondrial mbrane ATP synthase (F1F0 ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the mbrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F1 – containing the extrambraneous catalytic core, and F0 – containing the mbrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP turnover in the catalytic domain of F1 is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F1 domain and of the central stalk which is part of the complex rotary elent. Rotation of the central stalk against the surrounding alpha3beta3 subunits leads to hydrolysis of ATP in three separate catalytic sites on the beta subunits. | |
Limitations and Performance Guarantee
This is a life science research product (for Research Use Only). This product is guaranteed to work for a period of two years when stored at -70C or colder, and one year when aliquoted and stored at -20C.




There are no reviews yet.