Human ATP5J, mitochondrial Recombinant Protein Product Attributes
Product Type: Recombinant Protein
Recombinant ATP5J, mitochondrial based upon sequence from Human
Host: QP5697 protein expressed in E. coli.
Tag: GST
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the Homo sapiens (Human) ATP5J, mitochondrial, was expressed in the hosts and tags indicated. Please select your host/tag option, above.
Recommended Applications: Immunogen, Protein Standard, Cell culture, or Other Cell Biology Applications.
Application Notes: Please contact us for application specific information for QP5697.
Bioactivity Data: Untested
Full Length? Full Length
Amino Acid Sequence: NKELDPIQKL FVDKIREYKS KRQTSGGPVD ASSEYQQELE RELFKLKQMF GNADMNTFPT FKFEDPKFEV IEKPQA
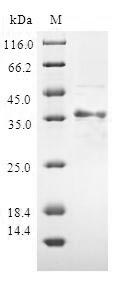
Purity: Greater than 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Reconstitution Instructions: Concentrated protein in liquid format. Reconstitution is not necessary.
Concentration of Human ATP5J, mitochondrial Protein:
Endotoxin Levels: Not determined.
Buffer: Tris-based buffer, 50% glycerol
Storage Conditions: Store at -20C to -80C.
| Recombinant Human ATP5J, mitochondrial Protein General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| ATP5, ATPM, ATP5A, F6, CF6, ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondri | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | ATP5J |
| Entrez Gene ID | 522 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000154723 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001003696.1 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001003696.1, NM_001003697.1, NM_001003701.1, NM_001003703.1, NM_001320266.1, NM_001320267.1, NM_001685.4 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P18859 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs.246310 |
| HGNC ID(s) | HGNC:847 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | ATP5J |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:522 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA25137 |
| General Description of Recombinant Human ATP5J, mitochondrial Protein. | |
| Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F1F0 ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F1 – containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F0 – containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F1 is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F0 domain and the peripheric stalk, which acts as a stator to hold the catalytic alpha3beta3 subcomplex and subunit a/ATP6 static relative to the rotary elements. Also involved in the restoration of oligomycin-sensitive ATPase activity to depleted F1-F0 complexes. | |
Limitations and Performance Guarantee
This is a life science research product (for Research Use Only). This product is guaranteed to work for a period of two years when stored at -70C or colder, and one year when aliquoted and stored at -20C.



There are no reviews yet.