Influenza Influenza B (strain B / Singapore / 222 / 1979) Nucleoprotein Recombinant Protein Product Attributes
Product Type: Recombinant Protein
Recombinant Influenza B (strain B / Singapore / 222 / 1979) Nucleoprotein based upon sequence from: Influenza
Host: QP7284 protein expressed in E.coli, Yeast..
Tag: GST
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the Influenza B virus (strain B/Singapore/222/1979) Influenza B (strain B/Singapore/222/1979) Nucleoprotein, was expressed in the hosts and tags indicated. Please select your host/tag option, above.
Application Notes: Please contact us for application specific information for QP7284.
Bioactivity Data: Untested
Full Length? Extracellular Domain
Expression Region: Met1 – Pro168
Amino Acid Sequence: MSNMDIDGIN TGTIDKTPEE IISGTSGATR PIIRPATLAP PSNKRTRNPS PERATTSSEA DVGRKTQKKQ TPTEIKKSVY NMVVKLGEFY NQMMVKAGLN DDMERNLIQN AHAVERILLA ATDDKKTEFQ KKKNARDVKE GKEEIDHNKT GGTFYKMVRD DKTIYFSP
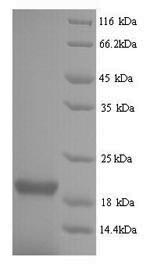
Purity: Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Reconstitution Instructions:
Concentration of Influenza Influenza B (strain B / Singapore / 222 / 1979) Nucleoprotein Protein:
Endotoxin Levels: Not determined.
Buffer: Tris-based buffer, 50% glycerol
Storage Conditions: Store at -20C to -80C.
| Recombinant Influenza Influenza B (strain B / Singapore / 222 / 1979) Nucleoprotein Protein General Information | |
|---|---|
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | NP |
| UniProt ID(s) | P04666 |
| General Description of Recombinant Influenza Influenza B (strain B / Singapore / 222 / 1979) Nucleoprotein Protein. | |
| Encapsidates the negative strand viral RNA, protecting it from nucleases. The encapsidated genomic RNA is termed the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) and serves as tplate for transcription and replication. The RNP needs to be localized in the nucleus to start an infectious cycle, but is too large to diffuse through the nuclear pore complex. NP comprises at least 2 nuclear localization signals and is responsible of the active RNP import into the nucleus through the cellular importin alpha/beta pathway. Later in the infection, nucleus export of RNP are mediated through viral proteins NEP interacting with M1 which binds nucleoproteins. It is possible that the nucleoprotein binds directly exportin-1 (XPO1) and plays an active role in RNP nuclear export. M1 interaction with RNP ses to hide nucleoprotein’s nuclear localization signals. Soon after a virion infects a new cell, M1 dissociates from the RNP under acidification of the virion driven by M2 protein. Dissociation of M1 from RNP unmask nucleoprotein’s nuclear localization signals, targeting the RNP to the nucleus . | |
Limitations and Performance Guarantee
This is a life science research product (for Research Use Only). This product is guaranteed to work for a period of two years when stored at -70C or colder, and one year when aliquoted and stored at -20C.




There are no reviews yet.