Human SMARCB1 Recombinant Protein Product Attributes
Product Type: Recombinant Protein
Recombinant SMARCB1 based upon sequence from: Human
Host: QP7605 protein expressed in Baculovirus, Yeast, E.coli..
Tag: His
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the Homo sapiens (Human) SMARCB1, was expressed in the hosts and tags indicated. Please select your host/tag option, above.
Application Notes: Please contact us for application specific information for QP7605.
Bioactivity Data: Untested
Full Length? Partial (see sequence information for more details).
Expression Region: Met2 – Arg376
Amino Acid Sequence: MMMALSKTFG QKPVKFQLED DGEFYMIGSE VGNYLRMFRG SLYKRYPSLW RRLATVEERK KIVASSHGKK TKPNTKDHGY TTLATSVTLL KASEVEEILD GNDEKYKAVS ISTEPPTYLR EQKAKRNSQW VPTLPNSSHH LDAVPCSTTI NRNRMGRDKK RTFPLCFDDH DPAVIHENAS QPEVLVPIRL DMEIDGQKLR DAFTWNMNEK LMTPEMFSEI LCDDLDLNPL TFVPAIASAI RQQIESYPTD SILEDQSDQR VIIKLNIHVG NISLVDQFEW DMSEKENSPE KFALKLCSEL GLGGEFVTTI AYSIRGQLSW HQKTYAFSEN PLPTVEIAIR NTGDADQWCP LLETLTDAEM EKKIRDQDRN TRRMR
Purity: Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Reconstitution Instructions:
Concentration of Human SMARCB1 Protein:
Endotoxin Levels: Not determined.
Buffer: Tris-based buffer, 50% glycerol
Storage Conditions: Store at -20C to -80C.
| Recombinant Human SMARCB1 Protein General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| MRD15; Snr1; CSS3; INI1; RDT; RTPS1; SWNTS1; PPP1R144; SNF5; Sfh1p; SNF5L1; BAF47; hSNFS; SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily B member | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | SMARCB1 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 6598 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000099956 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001007469.1 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001007468.2, NM_003073.4 |
| UniProt ID(s) | Q12824 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs.534350 |
| HGNC ID(s) | HGNC:11103 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | SMARCB1 |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:6598 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA35953 |
| General Description of Recombinant Human SMARCB1 Protein. | |
| Core component of the BAF (hSWI/SNF) complex. This ATP-dependent chromatin-rodeling complex plays important roles in cell proliferation and differentiation, in cellular antiviral activities and inhibition of tumor formation. The BAF complex is able to create a stable, altered form of chromatin that constrains fewer negative supercoils than normal. This change in supercoiling would be due to the conversion of up to one-half of the nucleosomes on polynucleosomal arrays into asymmetric structures, termed altosomes, each composed of 2 histones octamers. Stimulates in vitro the rodeling activity of SMARCA4/BRG1/BAF190A. Involved in activation of CSF1 promoter. Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin rodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron-specific chromatin rodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development a switch from a st/progenitor to a post-mitotic chromatin rodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural st/progenitor cells to post-mitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural st cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth . Plays a key role in cell-cycle control and causes cell cycle arrest in G0/G1. | |
Limitations and Performance Guarantee
This is a life science research product (for Research Use Only). This product is guaranteed to work for a period of two years when stored at -70C or colder, and one year when aliquoted and stored at -20C.

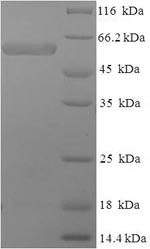

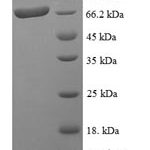

There are no reviews yet.