Human, Mouse (-), and Rat (-) Anti-p21WAF1 Antibody Product Attributes
p21WAF1 Previously Observed Antibody Staining Patterns
Observed Subcellular, Organelle Specific Staining Data:
Anti-CDKN1A antibody staining is expected to be primarily localized to the nuclear bodies and nucleoplasm. There is variability in either the signal strength or the localization of signal in nuclear bodies, and nucleoplasm from cell to cell.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Type:
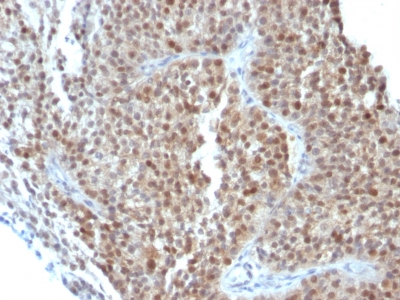
Variations in p21WAF1 antibody staining intensity in immunohistochemistry on tissue sections are present across different anatomical locations. An intense signal was observed in Leydig cells in the testis, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine and vagina and trophoblastic cells in the placenta. More moderate antibody staining intensity was present in Leydig cells in the testis, respiratory epithelial cells in the bronchus, squamous epithelial cells in the cervix, uterine and vagina and trophoblastic cells in the placenta. Low, but measureable presence of p21WAF1 could be seen in cells in the glomeruli in kidney, cells in the red pulp in spleen, cells in the tubules in kidney, exocrine glandular cells in the pancreas, germinal center cells in the lymph node, glandular cells in the breast, fallopian tube, gallbladder, parathyroid gland, prostate, seminal vesicle and stomach, hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow, hepatocytes in liver, keratinocytes in skin, non-germinal center cells in the lymph node and tonsil and respiratory epithelial cells in the nasopharynx. We were unable to detect p21WAF1 in other tissues. Disease states, inflammation, and other physiological changes can have a substantial impact on antibody staining patterns. These measurements were all taken in tissues deemed normal or from patients without known disease.
Observed Antibody Staining Data By Tissue Disease Status:
Tissues from cancer patients, for instance, have their own distinct pattern of p21WAF1 expression as measured by anti-p21WAF1 antibody immunohistochemical staining. The average level of expression by tumor is summarized in the table below. The variability row represents patient to patient variability in IHC staining.
| Sample Type | breast cancer | carcinoid | cervical cancer | colorectal cancer | endometrial cancer | glioma | head and neck cancer | liver cancer | lung cancer | lymphoma | melanoma | ovarian cancer | pancreatic cancer | prostate cancer | renal cancer | skin cancer | stomach cancer | testicular cancer | thyroid cancer | urothelial cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Intensity | – | – | +++ | + | ++ | – | ++ | – | + | – | + | – | + | – | + | ++ | + | – | + | ++ |
| CDKN1A Variability | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ |
| p21WAF1 General Information | |
|---|---|
| Alternate Names | |
| cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1, CDK-interacting protein 1, p21Cip1, p21 Cip1, p21Waf1, p21 Waf1 | |
| Molecular Weight | |
| 21kDa | |
| Chromosomal Location | |
| 6p21.31 | |
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | CDKN1A |
| Entrez Gene ID | 1026 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000124762 |
| RefSeq Protein Accession(s) | NP_001207706, NP_000380, NP_001207707, NP_001278478, NP_510867 |
| RefSeq mRNA Accession(s) | NM_001291549, NM_001220778, NM_000389, NM_078467, NM_001220777 |
| RefSeq Genomic Accession(s) | NG_009364, NC_000006, NC_018917 |
| UniProt ID(s) | A0A024RCX5, P38936 |
| UniGene ID(s) | A0A024RCX5, P38936 |
| HGNC ID(s) | 1784 |
| Cosmic ID(s) | CDKN1A |
| KEGG Gene ID(s) | hsa:1026 |
| PharmGKB ID(s) | PA104 |
| General Description of p21WAF1. | |
| This MAb recognizes a 21kDa protein, identified as the p21WAF1 tumor suppressor protein. This MAb is highly specific to p21, shows no cross-reaction with other closely related mitotic inhibitors. p21WAF1 is a specific inhibitor of cdks, a tumor suppressor involved in the pathogenesis of a variety of malignancies. The expression of this gene acts as an inhibitor of the cell cycle during G1 phase, is tightly controlled by the tumor suppressor protein p53. Its expression is induced by the wild type, but not mutant, p53 suppressor protein. Normal cells generally display a rather intense nuclear p21 expression. Loss of p21 expression has been reported in many carcinomas (gastric carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, thyroid carcinoma). | |

.jpg)

-150x150.jpg)
-150x150.jpg)
-150x150.jpg)
-150x150.jpg)
-150x150.jpg)

There are no reviews yet.