Human HLA-DRB Recombinant Protein Product Attributes
Product Type: Recombinant Protein
Recombinant HLA-DRB based upon sequence from: Human
Host: QP7354 protein expressed in E. coli.
Tag: HIs-Myc
Protein Construction: A DNA sequence encoding the Homo sapiens (Human) HLA-DRB, was expressed in the hosts and tags indicated. Please select your host/tag option, above.
Application Notes: Please contact us for application specific information for QP7354.
Bioactivity Data: Untested
Full Length? Extracellular Domain
Expression Region: Gly30 – Lys227
Amino Acid Sequence: GDTRPRFLWQ LKFECHFFNG TERVRLLERC IYNQEESVRF DSDVGEYRAV TELGRPDAEY WNSQKDLLEQ RRAAVDTYCR HNYGVGESFT VQRRVEPKVT VYPSKTQPLQ HHNLLVCSVS GFYPGSIEVR WFRNGQEEKA GVVSTGLIQN GDWTFQTLVM LETVPRSGEV YTCQVEHPSV TSPLTVEWRA RSESAQSK
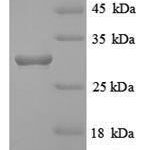
Purity: Greater than 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Reconstitution Instructions:
Concentration of Human HLA-DRB Protein:
Endotoxin Levels: Not determined.
Buffer: Tris-based buffer, 50% glycerol
Storage Conditions: Store at -20C to -80C.
| Recombinant Human HLA-DRB Protein (30-227aa) General Information | |
|---|---|
| Curated Database and Bioinformatic Data | |
| Gene Symbol | HLA-DRB1 |
| Ensemble Gene ID | ENSG00000196126 |
| UniProt ID(s) | P04229 |
| UniGene ID(s) | Hs.534322 |
| HGNC ID(s) | HGNC:4948 |
| COSMIC ID Link(s) | HLA-DRB1 |
| General Description of Recombinant Human HLA-DRB Protein (30-227aa). | |
| Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route; where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules; and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments; exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides; autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs; other cells of the gastrointestinal tract; such as epithelial cells; express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs; which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen; three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs; CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases; including CTSS and CTSL; leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells; the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal microenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules; increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading. (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Epstein-Barr virus on lymphocytes. |
|
Limitations and Performance Guarantee
This is a life science research product (for Research Use Only). This product is guaranteed to work for a period of two years when stored at -70C or colder, and one year when aliquoted and stored at -20C.





There are no reviews yet.